
The main line of AI in 2026 is clear: computing power as the foundation, mobile phones breaking the situation, with four major explosive points in place

In 2026, the field of artificial intelligence will undergo significant changes, with computing power continuously strengthening, and smartphones will become the core of AI assistants. Google's Gemini 3 has made significant progress in reasoning and multimodal capabilities, making the explosion of AI smartphones inevitable. ByteDance plans to release an AI smartphone assistant in 2025, showcasing the potential for cross-application operations. Overall, computing power and algorithm innovation will drive the rapid iteration of AI applications, expected to trigger fierce competition among global tech giants
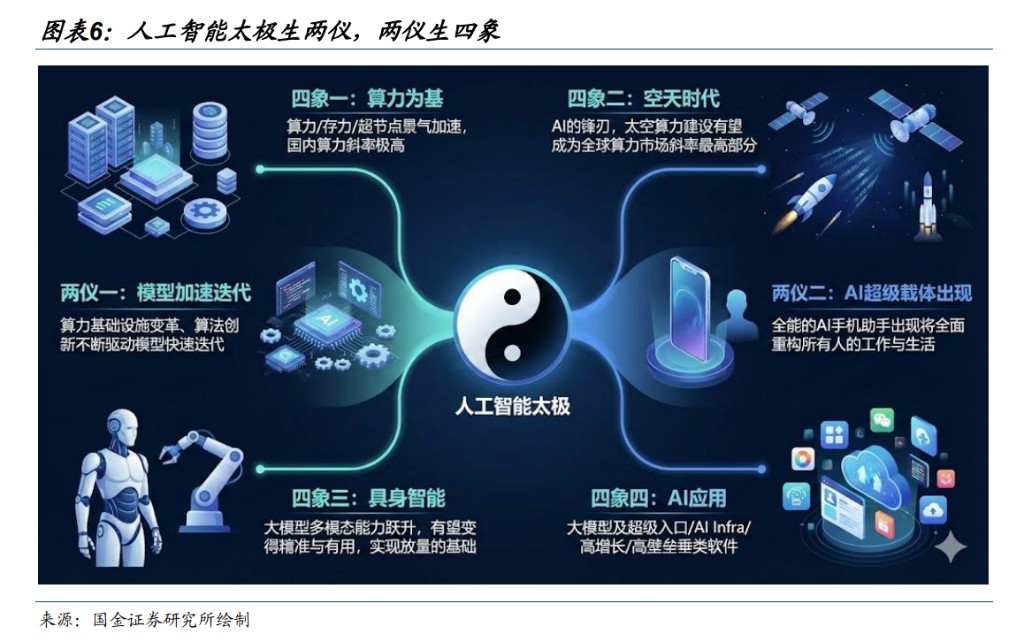
- In 2026, the AI computing rate will gradually accelerate, with a layout in the artificial intelligence sector, and the intersection gap between model acceleration iteration and AI ultra-short-term systems will emerge. 1) The chaotic transformation of algorithmic foundations, with continuous innovation in algorithm details driving rapid iteration of models. Breakthroughs in large-scale packaging by global top players, with Google Gemini 3 achieving a leap in basic reasoning and multimodal capabilities, the most critical metric of screen understanding accuracy increasing from 11.4% in the previous generation to 72.7%, indicating that the explosion of AI smartphones has become inevitable. At the same time, intelligent models may be able to understand natural language commands and transform into multifunctional robots in various scenarios within three years; algorithmic innovation remains frequent; the domestic open-source model DeepSeek-V3.2 Speciale demonstrates significant breakthroughs in algorithm and training paradigms through top-tier closed-loop models, refined attention (DSA), high ratio post-training, and large-scale synthetic data innovations, predicting that the training and scaling law has not yet reached a bottleneck; currently, model training is still primarily based on the physical Hopper series and Google TPU V3, V5, and with the integration of the physical Blackwell cluster and Google TPU V7 coming into use, large-scale iterations in 2026 will still be exciting. 2) The AI ultra-short-term system is emerging: smartphones themselves are the culmination of information flow in people's work and life, and the emergence of an all-purpose AI assistant will face unprecedented tasks and challenges. ByteDance will release a technical preview of the AI smartphone assistant in December 2025, enabling AI to autonomously operate across applications on smartphones. Although there are still shortcomings, it has already shown all-purpose potential, forming a data flywheel and beginning rapid iteration. Breakthroughs in GUI technology have mechanized the expansion gaps formed in the API era, and AI smartphones are a prerequisite for the explosion of other AI terminals, with global top manufacturers expected to significantly engage in this new entry battle. 3) The two instruments give rise to the four phenomena: computing power as the foundation, the era of air and space, with intelligence and continuous exciting AI applications.
Phenomenon One: Everything still points to computing power, with computing power/extraordinary power/super node systems accelerating, and domestic computing power competition remains unresolved. 1) Scaling Law shifts from pre-training to three-dimensional modeling of pre/post/test-time, adding a new reasoning model of interleaved thinking, with both training and reasoning computing power being logically strong. 2) The AI smartphone drives the entry battle, with no manufacturers able to share; Tencent and Huawei have recently made significant investments. It is expected that global manufacturers will invest sufficiently in high-end capacities, with current statistics showing cash flow pressure among mainstream manufacturers. 3) Domestic computing power: domestic GPU performance surpasses H20, requiring high-precision chips before going public, with domestic GPU manufacturers like "Cool" rapidly closing the loop. Market prices are accelerating over the 26 years; 4) Storage: The widespread application of multimodal penetration and KV Cache, with storage latency still transforming to "fast" and "high," with prices and demand continuing to rise;5) Supernodes: Supernodes compensate for resource shortages and high latency issues through high-speed interconnection, becoming the new normal for AI infrastructure, with domestic GPU manufacturers accelerating their layout.
Quadrant Two: The aerospace era and the popularization of AI. 1) On the overseas front, institutions such as NVIDIA, Google, and SpaceX are investing heavily in large-scale computing power construction, and SpaceX is expected to achieve the largest IPO in history, with a valuation of up to $15 trillion, becoming a key player in the nearly $10 billion market growth of the world's first $600 billion market. 2) On the policy front: Recent supportive policies have emerged, emphasizing aerospace development in the "14th Five-Year Plan." Data from the National Maritime Administration in 2025 indicates that China's mainland satellite navigation program is expected to reach a peak, with significant policies continuously allowing commercial rocket companies to use camera-driven cloud platforms to enter the market. 3) On the domestic front, we are actively planning multiple low-energy satellite constellations and have planned a three-body computing constellation to participate in the space computing competition with the Beijing Space Data Center. 4) Breakthroughs in our reusable rocket technology are nearing, with the "national team" and the public actively focusing on competition, and key flights are gradually breaking through.
Quadrant Three: Intelligent support for precise layout, achieving efficiency as a foundation. 1) Tesla's Optimus V3 is nearing release, expected to be the largest cost for the development of robotic brains, with rapid improvements in task accuracy. 2) Significant model reductions, Gemini 3 Opro signifies a leap in large-scale multimodal understanding capabilities, enabling future robots to understand various human commands and complete positioning tasks in combination with scenarios, not only making it possible but also providing a foundation for intelligent algorithm attacks. 3) From an industrial signal perspective, Tesla's drones are expected to mark the beginning of a year of reverse mass production, becoming the starting point for everything.
Quadrant Four: AI applications grow, and the tsunami of big data AI infrastructure will bring high-barrier parameter software worth paying attention to. 1) Model iteration and application deepening, whether it is B-end token calls further exploding. 2) The computer industry will be at historical lows, with conditions for trading and rebound. 3) The revenue and profit growth rates of the computer industry are expected to bottom out in early 2025, with more obvious transformation possibilities driven by AI. It is recommended to focus on two types of high-efficiency solutions in iterative fields: first, large-scale dual-layer embedded systems, where leading module manufacturers see an increase in high-end ARR and token consumption, based on personalized and ecological integration into enterprise intelligent products; second, AI infrastructure, as a key intermediary layer connecting models and implementation, directly determining the cost and effectiveness limits of AI usage. The high growth performance of Databricks and Snowflake can validate the high-value attributes of this segment; third, high-growth software categories: dynamic bandwidth, advertising, medical, and other business AIs are all showing rapid growth potential; fourth, high-barrier parameter software, relying on industry know-how, proprietary data, complex processes, and compliance integration, such applications can sustain models as amplifiers of decision-making capabilities, achieving value leaps while avoiding disruptionOther key segments: 1) 3D Printing: Currently, new videos are emerging, marking the beginning of 3D printing. The Chinese 3D printing market was previously impacted by the pandemic, and by 2034, the global market size is expected to exceed USD 11.45 billion. We believe that as industries such as AI, aerospace, 3C, robotics, and automotive continue to break through innovation trends, traditional manufacturing processes are nearing their limits and are struggling to meet practical demands such as heat dissipation and lightweighting. To date, breakthroughs in 3D printing technology remain limited, and the explosion of multidimensional demands is expected to accelerate industry development. 2) Financial IT: Reducing cycles and global capital activity, the rise of cross-border Alipay finance. The expectation of interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve in 2026 is likely to boost trading activity in capital markets; the "14th Five-Year Plan" clearly outlines the quality development of capital markets, and capital market IT is expected to usher in a new phase of rapid development. Global cross-border payment innovations are accelerating transformation, opening up space for the broader promotion and application of the digital renminbi. 3) Intelligent Driving: Officially entering the industrialization stage. In September 2025, China's L2 strong chain will enter the public consultation phase. In December 2025, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology officially announced the first batch of L3 conditional autonomous driving vehicle access permits in China, marking the transition of L3 autonomous driving from the testing phase to industrial application. Over the past nine years, Pony.ai has been the first to achieve urban-level single vehicle UE model approval for Robotaxi in Guangzhou, and the China-U.S. Robotaxi fleets are on the brink of explosion. Intelligent driving models, represented by consumer behavior, are continuously iterating, with market share rapidly increasing.
I. AI Evolution Path Becomes Clearer
1.1 Rapid Iteration of Global Top Models
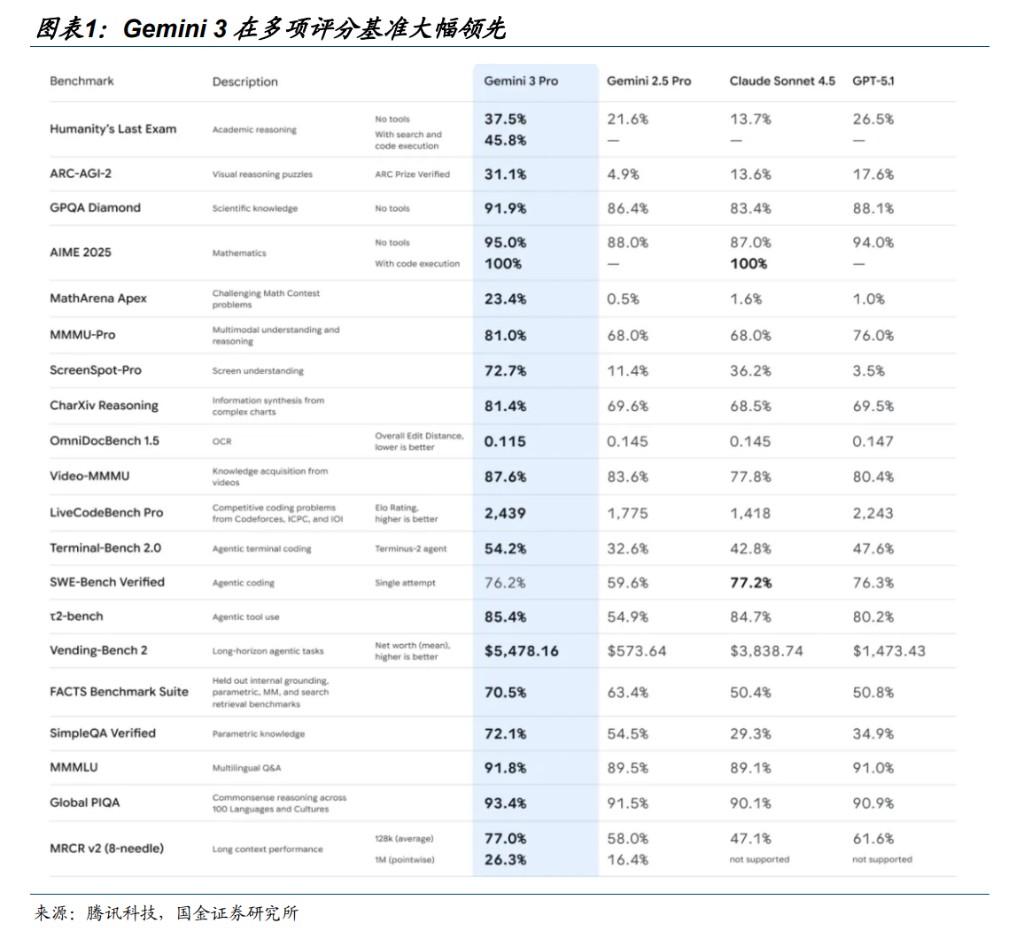
On November 19, 2025, Google Gemini 3 was released, achieving a leap in scoring improvement, with powerful multimodal understanding, more diverse UI, and advanced front-end capabilities, marking a significant step forward in the progress of large models.
In terms of basic reasoning ability, Humanity’s Last Exam is the ultimate test of whether AI can solve humanity's top challenges. Before Gemini 3, Gemini 2.5 Pro scored 21.6%, while Claude Sonnet 4.5 only scored 13.7%. Gemini 3 Pro delivered answers with scores of 37.5% (without tools) and 45.8% (with tools). The ARC-AGI-2 test aims to measure the model's ability to handle novel reasoning tasks that it has never encountered before, rather than rote memorization. Gemini 3 Pro achieved a score of 31.1%, while GPT-5.1 only scored 17.6%. Gemini 2.5 Pro scored just 4.9%. This indicates that it is beginning to exhibit a form of fluid intelligence close to that of humans, capable of abstract reasoning in areas without extensive training data coverage.
In the multimodal field, Gemini 3 is particularly impressive, with scores of 81.0% in MMMU-Pro and 81.4% in CharXiv Reasoning, both surpassing competitors. In the screenshot understanding test ScreenSpot-Pro, Gemini 3 scored twice that of Claude Sonnet 4.5 and twenty times that of GPT-5.1This is crucial for building AI agents that can truly understand and operate graphical interfaces.
On December 11, 2025, OpenAI released GPT-5.2, a top model designed for professional work.
GPT-5.2 aims to bring more economic value to people. The model performs better in creating spreadsheets, designing presentations, writing code, recognizing images, understanding long text contexts, using tools, and handling complex multi-step projects.
The GDPvali assessment covers 44 occupations and is used to measure explicit knowledge-based work tasks. In the GDPval test, the model attempts to complete cross-explicit knowledge-based work, covering 44 occupations in the 9 industries that contribute the most to the U.S. GDP. The tasks require generating real work outputs, such as sales presentations, accounting spreadsheets, emergency scheduling reports, manufacturing charts, or short videos. According to results from human expert reviews, GPT-5.2 Thinking outperformed or matched industry-leading experts on 70.7% of high-difficulty knowledge-based work tasks. These tasks include creating presentations, spreadsheets, and other professional products. GPT-5.2 Thinking completes tasks at a speed approximately 3 times that of experts, while the cost is only about 1%.
On December 1, DeepSeek-V3.2 was officially released, with domestic models leading open-source innovation.
In publicly available reasoning Benchmark tests, DeepSeek-V3.2 reached the level of GPT-5, slightly below Gemini-3.0-Pro; DeepSeek-V3.2-Speciale is an enhanced version of DeepSeek-V3.2 for long thinking, showing significant performance in mainstream reasoning tests. Gemini-3.0-Pro successfully won full solutions for IMO 2025 (International Mathematical Olympiad), CMO 2025 (Chinese Mathematical Olympiad), ICPC World Finals 2025 (International Collegiate Programming Contest Global Finals), and IOI 2025 (International Olympiad in Informatics). Among them, the ICPC and IOI scores reached the levels of second and tenth place winners, respectively.
The DeepSeek V3.2 series models propose several innovations: continuing to use the DSA sparse attention mechanism, enhanced post-training, and large-scale synthetic data.
DSA stands for DeepSeek Sparse Attention, aimed at reducing computational complexity while maintaining model performance in contextual scenarios. For example, when you have an extremely thick book (assuming it has tens of thousands of pages), and you need to query specific information from it, requiring you to look at one page at a time and remember what you've seen, this is the dilemma traditional AI models face when processing long texts—the computational load grows quadratically with the length of the textThe role of DSA is to transform this "needle in a haystack" approach into "precise positioning," allowing focus only on the few pages most relevant to the target information, significantly enhancing the model's memory and understanding efficiency.
Additionally, DeepSeek realized that the continued inadequacy of open-source models in the later stages limited the model's task performance. Therefore, a more aggressive approach was adopted, aiming to improve the later-stage results by over 10% compared to the predicted effects.
This time, DeepSeek utilized large-scale synthetic agent data, primarily due to the lack of sufficiently diverse real training environments, which hindered the agents' task generalization capabilities. According to the evaluation results, using synthetic data significantly improved the model's generalization ability.
We believe that the model's iteration has not yet reached a bottleneck, and the progress of the model in 2026 will be even more exciting:
- The path of enhancing model capabilities through Scaling law remains effective.
After the training scale of DeepSeek-V3.2 expanded to 10% of the predicted effect, it is expected that this ratio will increase in the future. Moreover, the DeepSeek team noted in the paper that their training computing power is limited, and the breadth of world knowledge in DeepSeek-V3.2 still lags behind top closed-source models like Gemini 3 pro. The team plans to further enhance the predictive effects in the future. At the same time, the extensive use of synthetic data by DeepSeek effectively indicates that there is no need to worry about data bottlenecks.
The DSA mechanism proposed by DeepSeek-V3.2 demonstrates strong algorithmic innovation capabilities, alleviating concerns that large-scale technological innovations have reached a bottleneck.
Upgrades to the hardware foundation for large-scale training.
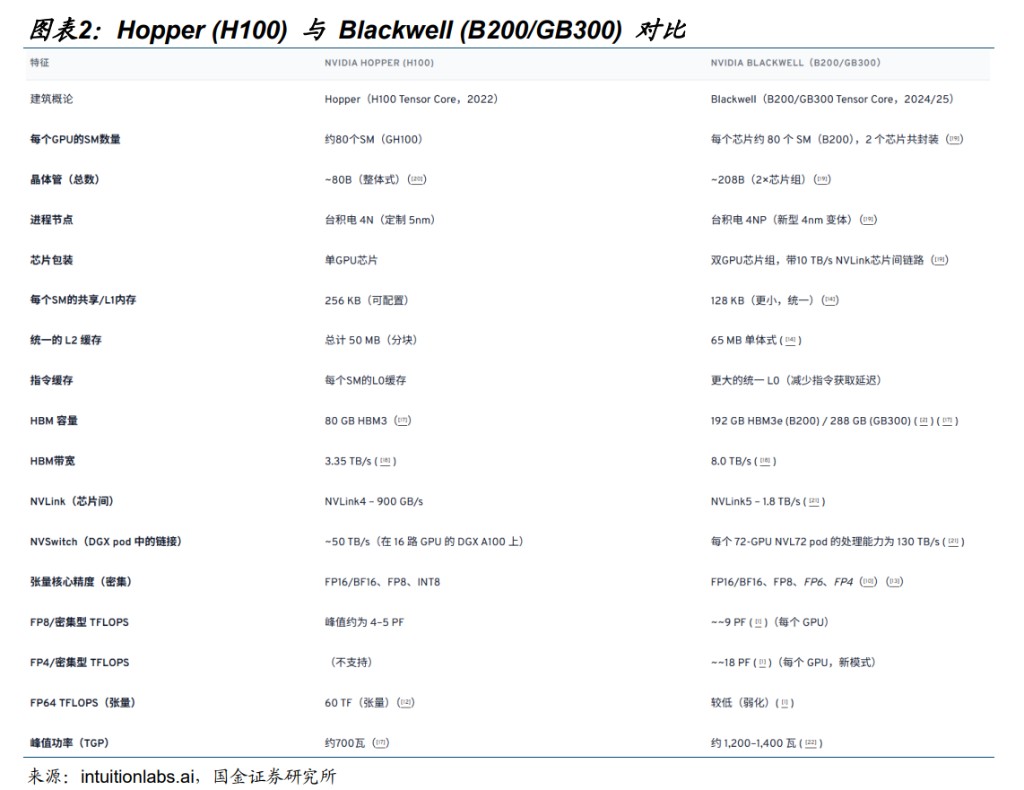
NVIDIA's Hopper architecture is transitioning to the Blackwell architecture, which significantly enhances single-card computing power, memory bandwidth, display capacity, and cluster interconnect compared to its predecessor. This has implications for large-scale training, as it accelerates and reduces costs while allowing for larger Batch Sizes (the number of training samples processed at once before model updates). This aids training stability, as larger Batch Sizes can more accurately estimate the overall data precision, making the learning process more stable. In contrast, smaller batches may produce excessively noisy and overly distinct signals, potentially leading to unstable jumps in the model's learning path.
Google also announced in November 2025 that its seventh-generation TPU Ironwood will be fully launched in the coming weeks. Ironwood is designed to handle the most demanding workloads: from large-scale model training and complex reinforcement learning to high-capacity, low-latency AI inference and model services, it can easily manage all of these tasks. Compared to TPU v5p, Ironwood's peak performance has increased tenfold; compared to TPU v6e (Trillium), its single-chip performance under training and inference workloads has improved by more than four times, making it Google's most powerful performance to dateThe most efficient custom chip. We believe that Google's chip upgrade will significantly promote model iteration.
1.2 ByteDance AI phone release, AI super carrier emerges
The phone itself is a culmination of people's work and life information flow, and the emergence of an all-purpose AI phone assistant will completely reshape everyone's work and life.
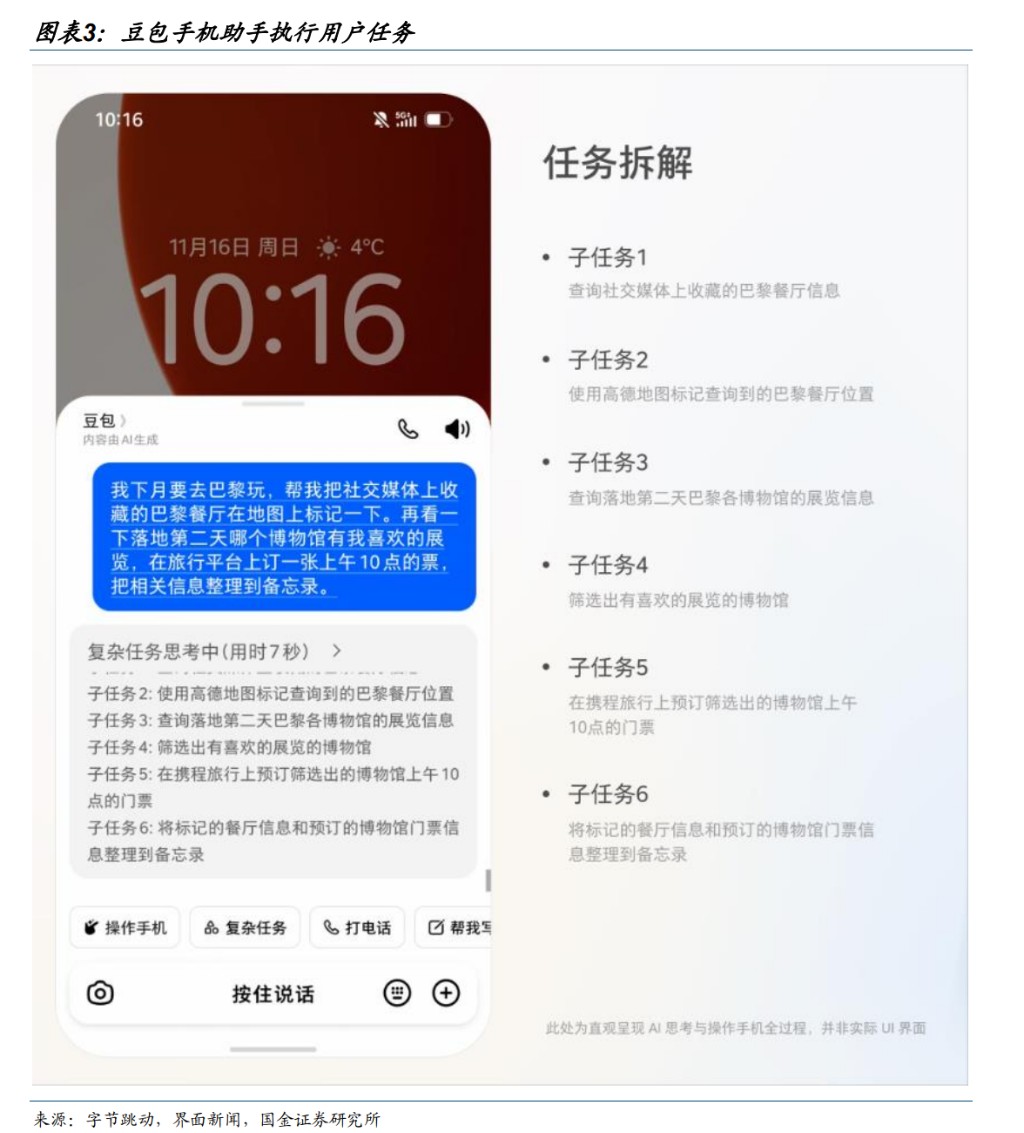
In December 2025, ByteDance released a technology preview of the five-color phone assistant on the prototype nubia M153 in collaboration with Peaceful Star. This version is currently available for a limited sale to developers and tech enthusiasts at a price of 3,499 yuan. Users can wake up the assistant directly through voice, side buttons, or the Ola Friend headset to interact and access features such as voice calls, video calls, and screen sharing. Additionally, the five-color phone assistant can directly control phone functions through AI, allowing users to input login numbers, place orders for products, and batch download files. The assistant can switch between multiple apps to help users search for the same products across platforms, compare prices, and select the cheapest products to order.
We believe that the five-color phone assistant is an important milestone in the evolution of AI from a single voice assistant to a truly actionable assistant on the consumer side. It not only understands user intentions but also autonomously executes complex tasks across applications, reflecting significant progress of AI in real-world scenarios and indicating that the way we interact with phones and user efficiency will be systematically reshaped.
Touch interaction based on graphical user interfaces (GUI) is the core interaction method of the mobile internet era, but it also has issues with complex operational processes and information integration between apps. Today, large models are driving a revolution in mobile interaction: users are liberated from complex clicks and transitions, only needing to issue natural language commands, and the AI Agent can complete tasks across application boundaries. Currently, the industry has formed two evolutionary logics on how to break application barriers:
API Agent route: Allowing developers to actively connect through standardized protocols. For example, Apple enables developers to integrate applications into Apple Intelligence through the App Intents framework.
GUI Agent route: Utilizing multimodal models to simulate human vision and operation. This method does not require developer cooperation and can directly operate various apps based on general visual capabilities, such as Doubao phone assistant.
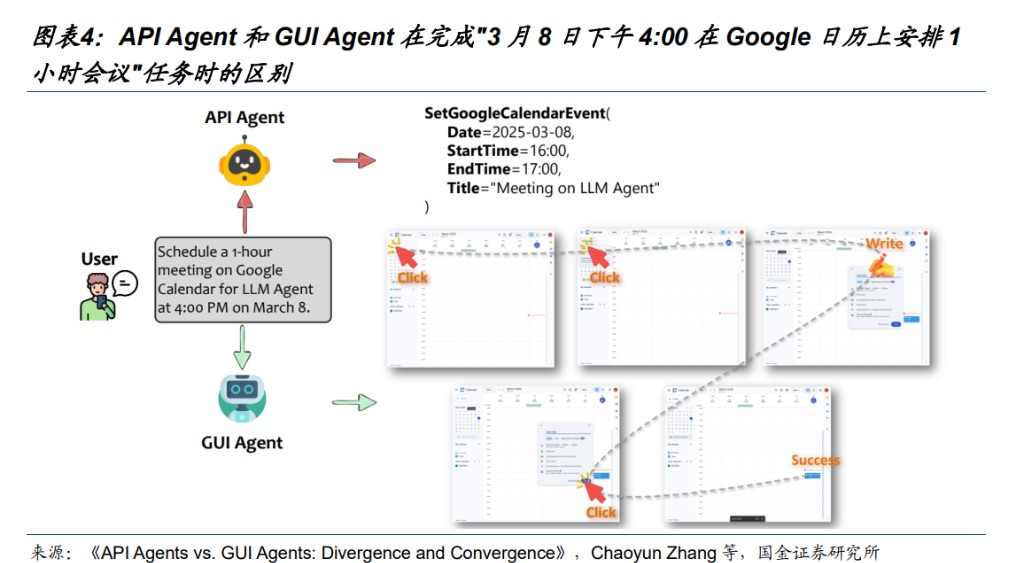
In terms of efficiency, privacy, and reliability, API Agents have advantages, but the core advantage of GUI Agents lies in their flexibility and universality, as they do not require application vendors to actively adapt, making them a powerful tool for breaking through fragmented application ecosystems. It is expected that model vendors, application vendors, and phone manufacturers will engage in fierce competition over traffic entry points in choosing between the two routes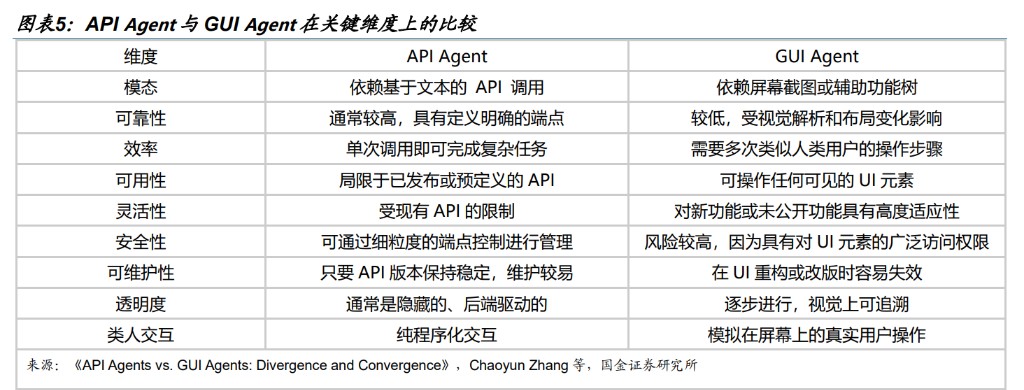
We believe that AI smartphones are a prerequisite for the explosion of other AI terminals, and it is expected that global top manufacturers will invest heavily in this new entry battle.
The two instruments have been set, and the four symbols are born: computing power as the foundation, the era of air and space, embodied intelligence, and continuous brilliance of AI applications. The rapid iteration of models and the aggregation of data streams by AI smartphones will drive clear investment opportunities in four areas by 2026. 1) The competition for computing power will become more intense, with a very high ceiling. 2) The air and space era will become the highest direction of competition in the field of computing power. 3) Robots may become capable of understanding speech and executing various tasks in conjunction with the environment. 4) The penetration rate of AI applications is approaching the axis measurement (5% to 20% is the new technology penetration rate axis).
II. Four Symbols One: Everything Still Points to Computing Power, 2026 is the Year of Domestic Computing Power Explosion
2.1 Everything still points to computing power, Scaling Law expands from training to inference
The three major Scaling Laws of large models: pre-training / post-training / test-time long thinking. The cycle of computing power and applications promotes: Computing Power Scaling -> Intelligence Improvement -> Widespread Adoption of Applications -> Economic Benefits -> Computing Power Scaling. After GPTo1, the model Scaling law shifts from a single pre-training to three major scalings. 1) The model generates a long internal thinking chain before responding to the user; the longer the thinking time, the higher the quality of the answer; 2) Multi-agent further enhances model performance, but its token consumption often reaches several times that of conversational chat.
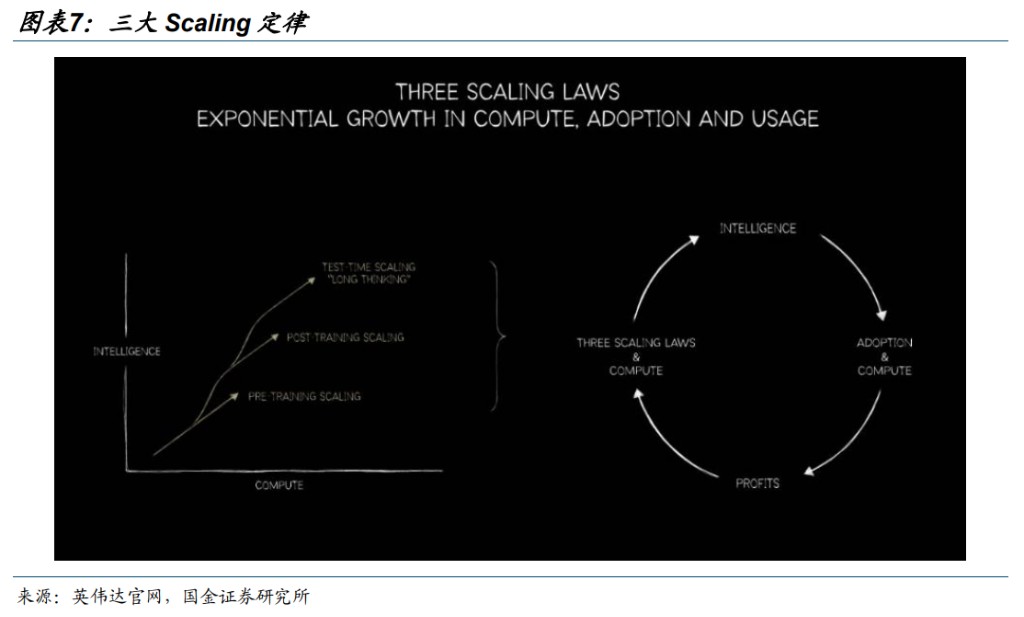
On the training level, pre-training restarts, and post-training intensifies. In terms of pre-training, the DeepSeek team admits in their paper that due to constraints on training computing power, the world knowledge breadth of DeepSeek-V3.2 still lags behind leading closed-source models (such as Gemini 3 Pro), and future efforts will focus on expanding the pre-training scale to fill the capability gap. Additionally, V3.2 often requires more tokens to approach the output quality of models like Gemini-3.0-Pro, and future focus will be on enhancing the "intelligence density" of the inference chain to achieve the same effect with fewer tokens;Post-training investment intensity increases: DeepSeek believes that the post-training investment in open-source models is generally insufficient and restricts task performance, thus raising the post-training computing budget to over 10% of the pre-training cost.
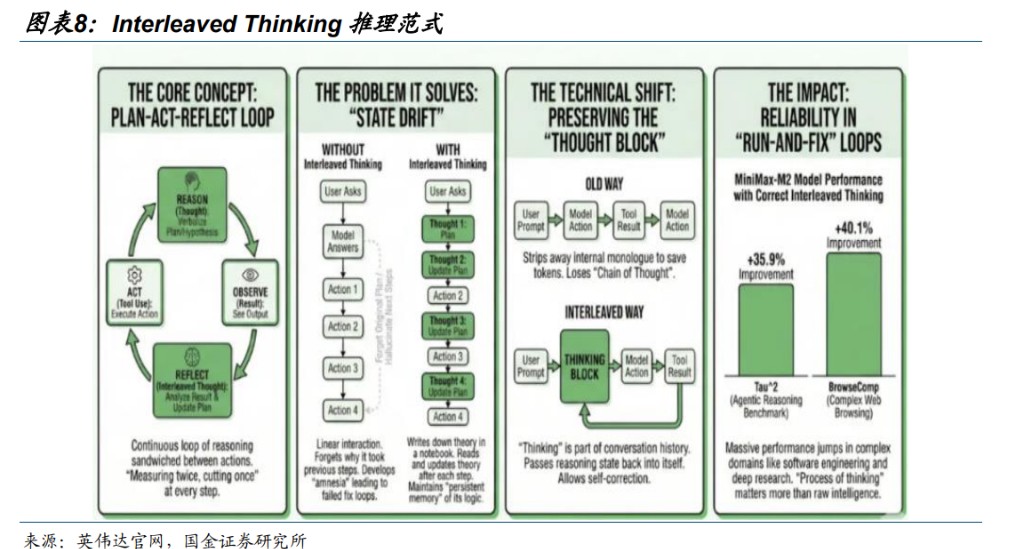
In terms of inference, domestic large models such as MiniMax M2 and DeepSeek V3.2 are integrating the dynamic cycle model of "thinking → acting → observing → rethinking" (Interleaved Thinking) into the inference process, becoming standard for Agent models. We believe that the penetration of the Interleaved Thinking paradigm in China can significantly improve the accuracy and planning capabilities of Agents, with token consumption and inference demand expected to accelerate in 2026.
2.2 Domestic GPUs: Continuous breakthroughs in capacity and performance, accelerating explosion in 2026
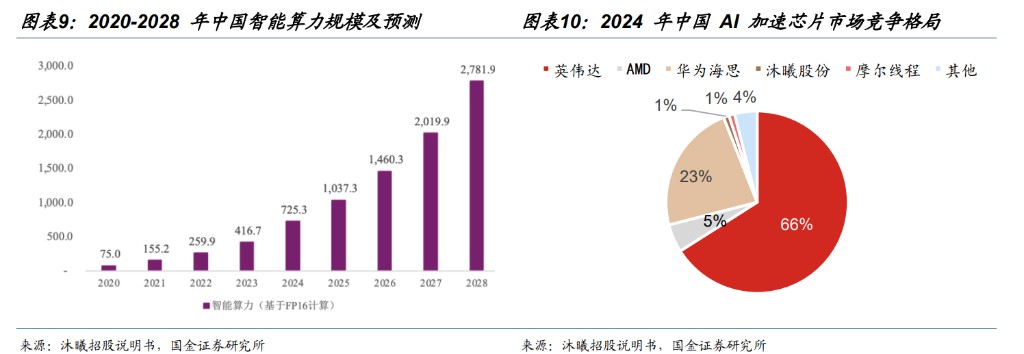
The intelligent computing center continues to expand, and domestic substitution accelerates. According to IDC data, China's intelligent computing scale was 75.0 EFLOPS in 2020, and it is expected to reach 2,781.9 EFLOPS by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate of 57.1% from 2020 to 2028. As geopolitical tensions drive Chinese companies to seek local alternatives and the steady improvement of domestic chip technology, domestic cloud service providers are accelerating the construction and architecture of core (combining different types of chips, such as CPU, GPU, and domestic substitute chips). For example, Tencent Cloud has fully compatible its heterogeneous computing platform with all mainstream domestic chips to meet internal development and customer demand for AI computing power. According to Bernstein Research, in the Chinese AI accelerator chip market in 2024, NVIDIA and AMD will have market shares of 66% and 5%, respectively, totaling 71%. However, benefiting from the trend of domestic substitution and supply chain security demands, domestic computing chip companies are rapidly improving. Among them, the market shares of Huawei HiSilicon/MuXi/Moore have reached 23%/1%/1%, respectively.
CSP manufacturers accelerate matching, aiding the construction of the domestic chip ecosystem. The reason NVIDIA's X86 ecosystem and CUDA ecosystem are difficult to shake is that they have formed a closed loop of "chip - software - application." Currently, in the domestic camp, companies like Huawei Yateng, Alibaba, and Bieqie Technology have different technical routes, and the ecological fragmentation issue is significant. Tencent Group's Senior Executive Vice President Tang Daosheng admitted in discussions that AI models of different parameter scales need to adapt to different chip configurations, and currently, scene coverage can only be achieved through cooperation with multiple manufacturers. Companies like Baidu and Alibaba are accelerating the matching of domestic chips to promote the formation of a closed loop of "chip - model - application."
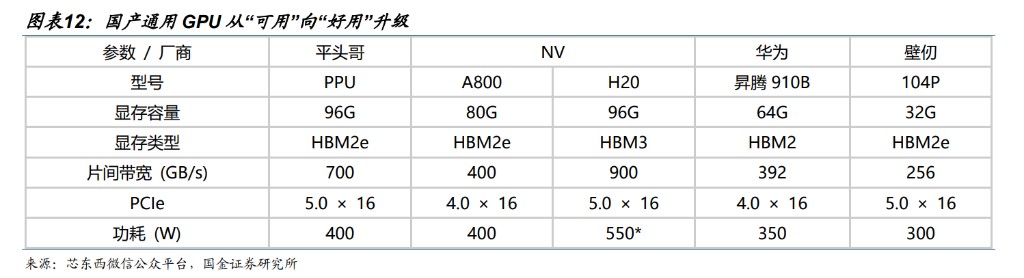
Domestic general-purpose GPUs are upgrading from "available" to "usable." Domestic GPUs still have gaps in performance metrics, software ecosystems, and application adaptations compared to NVIDIA's most advanced generation, but they are basically suitable for H20, A100, etc., and have advantages in localized services, policy support, and cost control. With continuous capital injection, domestic companies are expected to achieve breakthroughs in segmented scenarios and gradually expand their market share. 1) In terms of computing power metrics: Most leading domestic companies have mainstream products with FP16/BF16 around 100-300 TFLOPS, which is at the stage of NVIDIA's A100 products. A few manufacturers have achieved computing power close to NVIDIA's H100 products through advanced packaging, reaching the most advanced level in China; 2) In terms of video memory: Domestic companies choose HBM2e, HBM2, GDDR, and other types of video memory based on their product characteristics, with video memory bandwidth around 0.5-2 TB/s.
Supply side: Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC), as a leader in China's integrated circuits, continues to improve its capacity utilization rate. On November 13, SMIC disclosed its Q3 2025 financial report, showing revenue of 17.162 billion yuan, a quarter-on-quarter increase of 6.9%, and a gross margin of 25.5%; monthly capacity was 1.0228 million (equivalent to 8 inches), with a year-on-year increase of about 138,500 (equivalent to 8 inches); capacity utilization reached 95.8%, a quarter-on-quarter increase of 3.3 percentage points. SMIC's capacity is fully utilized, about one-third of TSMC's. The company's capital expenditure remains high, and future capacity will continue to increase.
2.3 The battle for entry has begun, and major companies are continuously increasing their investments.
The entry point is no longer limited to mobile phones but has evolved into a competition at the level of "OS-level intelligent agents" and "super apps." 1) The battle for entry among super apps has already begun. On December 24, 2025, ByteDance's AI application Doubao announced that its daily active users (DAU) exceeded 100 million; the Qianwen App has recently continued to expand its investment, and as of December 10 (23 days into public testing), its monthly active users have exceeded 30 million, making it the fastest-growing AI application globally. Alibaba mentioned in its market communication that the primary goal of the Qianwen C-end business group is to build Qianwen into a super app, becoming the first entry point for users in the AI era; 2) The "battle for entry" has driven the system permission layer from traffic distribution and has become the core of comprehensive and interactive upgrades, achieving an additional layer of "AI operating system" on top of the ecosystem through "screen viewing + quick operations."AIOS directly touches the commercial lifeline of super apps like WeChat and Alipay, challenging the game rules of the traditional app era. Super apps such as WeChat and Taobao have successively launched electronic machine permissions, but it is worth noting that brands like Huawei, Xiaomi, Honor, OPPO, and vivo have injected AI Agent capabilities into their flagship models. Model manufacturers are still expected to bypass app manufacturers' blockades through open-source and extensive alliances.

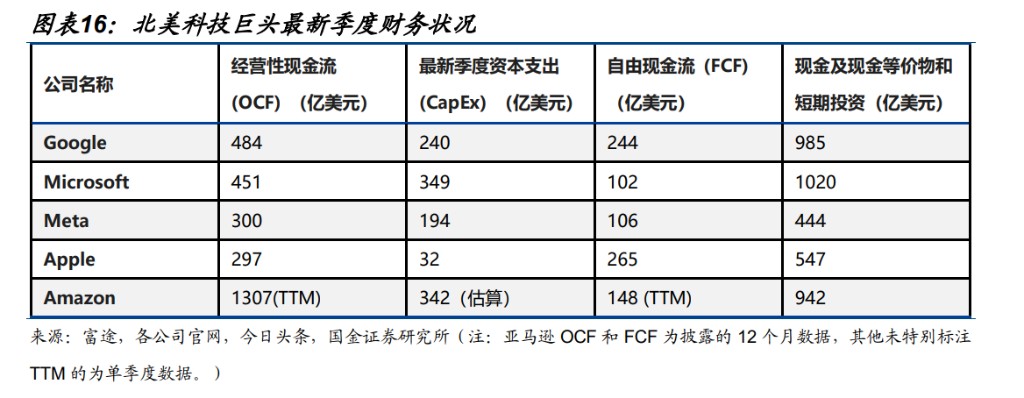
The global tech giants' arms race continues, with cash flow still supporting further investments. The investment of global tech giants in AI has entered an arms race stage. However, considering the free cash flow of each company and the cash flow transactions, short-term investors may be affected: excluding North American tech giant Meta, even assuming that the contribution of artificial intelligence (AI) to free cash flow has not fully manifested, the capital expenditure pressure for 2026 is expected to remain within a controllable range. At the same time, we believe that the certainty of AI demand is expected to train and enhance the return on invested capital (ROIC). Although a robust balance is still maintained in the future, with the outbreak of a large-scale financial crisis, the improvement of ROIC is driven by two factors: first, the continuous enhancement of model capabilities, including models, video generation models, and future global investment and financing, which are still breaking through, and the scalable development has not yet peaked, as evidenced by the progress of Google's Gemini 3 AI model. As model capabilities improve, the tasks that AI can undertake and the scenarios it can adapt to continue to increase. Second, the penetration rate of AI tasks across various industries is continuously rising, and the combination of these two major functions indicates a high certainty of AI demand growth within the next three years.
2.4 Storage: AI training/inference continues to drive storage demand
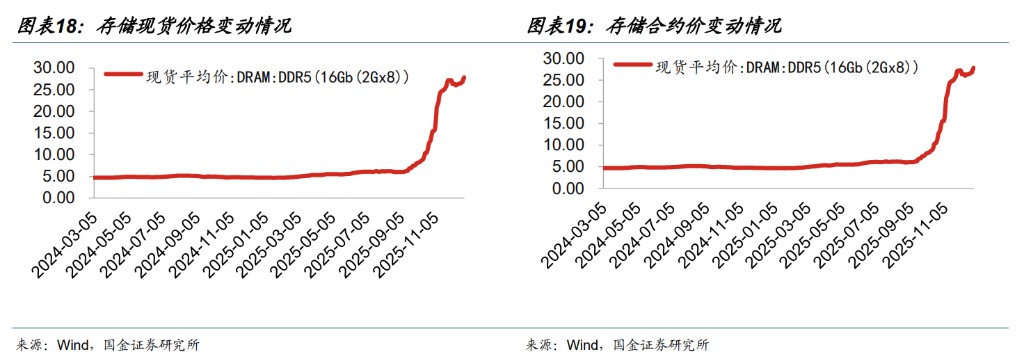
The inference of large AI models is driving rapid growth in storage demand. On the training side, SSDs are responsible not only for storing model parameters, including continuously updated weights and biases, but also for creating checkpoints to periodically save the AI model training progress, allowing recovery from specific points even if training is interrupted. On the inference side, it mainly includes three aspects: 1) LLM fast loading & KV caching: quickly loading model-related content and supporting KV caching to accelerate inference response; 2) Content store: the inference side requires content storage as online supply (understood as inference-oriented content/data storage); 3) RAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation introduces a "retrieval" inference loop, making the inference link more sensitive to storage access. The storage chip market is experiencing an unprecedented comprehensive surge in fast lending and price increases driven by AI. Entering the fourth quarter, there are signs of further intensification rather than a slowdown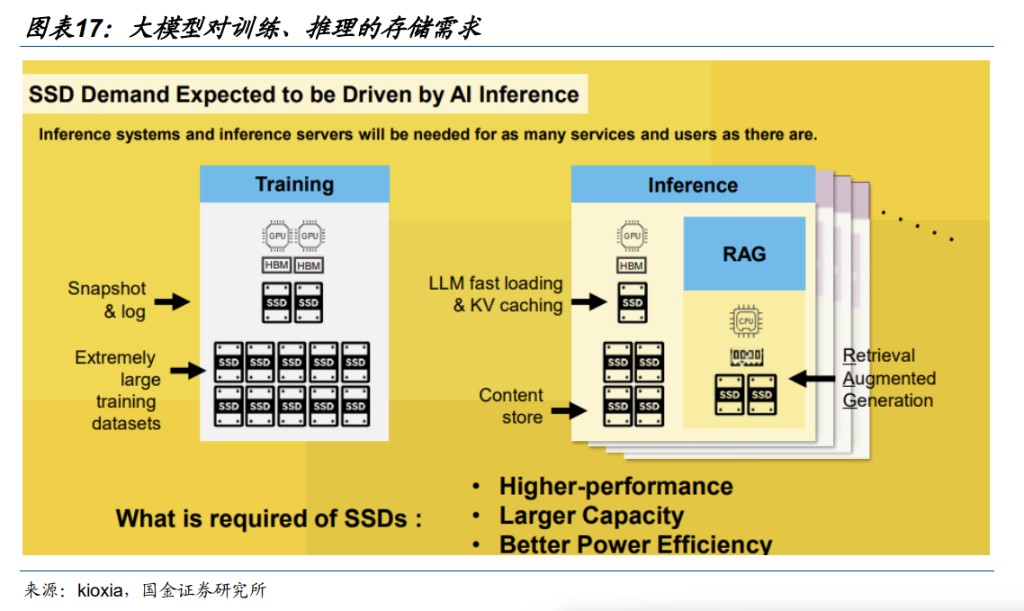
2.5 Super Nodes: Continuous breakthroughs in capacity + performance, accelerating explosion in 2026
Scale-up and Scale-out continue to expand. Large models require training using multi-machine and multi-card clusters, with mainstream parallel training methods including data parallelism, model parallelism (tensor parallelism, pipeline parallelism), and expert parallelism. The parallel computing methods of tensor parallelism and expert parallelism involve data volumes reaching hundreds of GB per iteration, necessitating high bandwidth and extremely low latency for GPU interconnections to reduce communication overhead costs between GPUs. As the parameter scale of large models grows exponentially, the effective computing power of a single card struggles to meet the demands of ultra-large-scale computing, making high bandwidth and low latency interconnect technology a key competitive factor, which also raises higher requirements for the interconnection topology of GPU clusters, driving the technological evolution of vertical scaling (Scale-up) and horizontal scaling (Scale-out) network architectures.
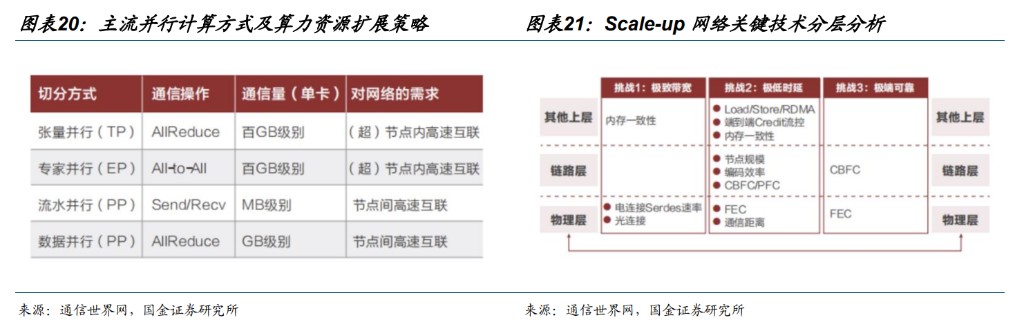
Domestic super nodes are being released one after another, with 2025 being the "accelerated penetration rate" for the super node industry. From Huawei's debut of the 384 super node host during the 2025 World Artificial Intelligence Conference to the unveiling of the scaleX ten-thousand-card super cluster system by Zhongke Lian on December 18, super nodes have accelerated from technological breakthroughs to product implementation. Leading companies such as Huawei, Zhongke Lian, Alibaba, and Baidu have all released super node products, while companies like ZTE, Inspur, H3C, and Super Fusion have followed suit with solutions, forming a comprehensive competitive landscape.
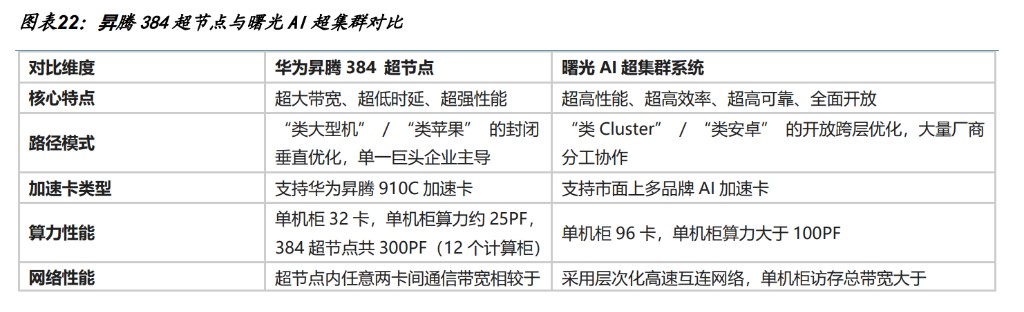
Three, Four Symbols II: Breakthrough of Rocket Bottlenecks Imminent, Space Computing Opens Application Space
3.1 Overseas Giants Compete for Space Computing, Opening a Trillion Dollar Market
NVIDIA has sent chips into space for the first time, marking the beginning of the space computing era. According to reports from Machine Heart, on November 2, 2025, NVIDIA sent the H100 GPU into space for the first time. This test flight was carried on the Starcloud-1 satellite of the startup Starcloud, marking the first step in the company's ambitious plan to migrate the world's energy-intensive data processing infrastructure to spaceThis three-year mission will be launched by SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket. The Starcloud-1 satellite, weighing only 60 kilograms, will operate in a super orbit approximately 350 kilometers from Earth. There, it will receive data from the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) Earth observation satellite constellation operated by the American company Capella, process this data in real-time, and transmit the information back to Earth. Starcloud even predicts that within the next decade, nearly all new data centers will be located in space, entirely due to limitations on terrestrial energy. A more powerful 100-kilowatt satellite is expected to be in orbit by 2027. Starcloud believes that by the early 2030s, it will have a 40-megawatt data center in space, with data processing costs comparable to those of data centers on Earth.
Google has disclosed "Project Suncatcher," entering the space computing market. According to Wall Street Watch, Google has revealed a plan called "Project Suncatcher," aimed at building a solar-powered space data center prototype. This project is not about establishing a single orbital monolith but rather a cluster of 81 satellites equipped with AI chips. They will fly in coordination in space and process data. As the first step of this plan, Google will collaborate with satellite company Planet, expecting to launch two prototype satellites to distant orbits by 2027. The core logic of this move is to leverage the unique environmental advantages of space—particularly the nearly constant solar energy provided by sun-synchronous orbits, as well as the land and water resources required for ground-based construction. For investors, this releases a clear signal: despite facing limitations in the physical world, the tech industry is still trying to prove that AI has unlimited scalability. If queries from AI models like Gemini can be processed in space and results sent back to Earth, it will fundamentally change the cost structure and energy dependence of their infrastructure.
Musk aims to achieve an annual deployment of 100GW of data centers through Starship in 4-5 years. According to federal reports, on November 4, 2025, Musk stated that he would expand the scale of Starship V3 satellites to build space data centers, aiming to achieve an annual deployment of 100GW of data centers through Starship in 4-5 years. Additionally, according to IT reports, Musk estimates that AI computing power may require a continuous power output of 200 to 300 kilowatts, or even close to 1 gigawatt. In comparison, a typical nuclear power plant can only provide about 1 gigawatt of continuous power, while the entire United States has a continuous generation capacity of only about 490 gigawatts. Therefore, Musk asserts that building such a scale of infrastructure to support AI on Earth is "impossible," and the only way out is in space.
 SpaceX, owned by Elon Musk, aims for a valuation as high as $1.5 trillion. According to Jiemian News, SpaceX is accelerating its initial public offering (IPO) plan, targeting a valuation of up to $1.5 trillion and plans to raise over $30 billion. If successful, SpaceX will surpass the $29 billion fundraising scale of oil giant Saudi Aramco, becoming the largest IPO in history.
SpaceX, owned by Elon Musk, aims for a valuation as high as $1.5 trillion. According to Jiemian News, SpaceX is accelerating its initial public offering (IPO) plan, targeting a valuation of up to $1.5 trillion and plans to raise over $30 billion. If successful, SpaceX will surpass the $29 billion fundraising scale of oil giant Saudi Aramco, becoming the largest IPO in history.
We believe that space computing is expected to become the fastest-growing segment in global computing. According to reports from the Science and Technology Innovation Board Daily, NVIDIA's financial performance in the second quarter of 2026 includes a global investment scale in data center infrastructure and computing expected to reach $600 billion this year alone, nearly doubling in two years. We believe that as American tech giants increasingly focus on space computing, it is likely to become the fastest-growing segment in global computing.
3.2 Recent aerospace support policies in China are expected to accelerate industry development
In 2014, China encouraged private capital to participate in space infrastructure construction, marking the beginning of the aerospace era. In November 2014, the State Council issued the "Guiding Opinions on Innovating Strategic Planning in Key Areas and Promoting Global Economic Development," which explicitly stated, "Encourage private capital to participate in national civil space infrastructure construction, improve the collection of satellite data for civil buildings, strengthen government procurement services, encourage private capital to develop, launch, and operate commercial facility satellites, and provide market-oriented, professional services. Guide private capital to participate in the construction of satellite navigation ground application systems." Subsequently, in 2015, the National Development and Reform Commission issued a notice on the "Medium and Long-term Development Plan for National Civil Space Infrastructure (2015-2025)," proposing to "explore new mechanisms for the market-oriented and commercial development of national civil space infrastructure, support the integration of future platforms with national civil space infrastructure construction and application development, actively carry out integration, transparency, and comprehensive application demonstrations in regional, industrial, international, and technological development, strengthen cross-domain resource sharing and information comprehensive service capabilities, accelerate integration with the Internet of Things, cloud computing, big data, and other new technologies and applications, promote sustainable development for satellite users, and enhance the overall support level and capability of China's space infrastructure for economic and social development."
Since then, the development of China's aerospace era has begun.
Commercial space has been continuously included in government work reports for 2024-2025, with increasing emphasis. The 2024 government work report proposed "actively creating emerging engines such as biomanufacturing, commercial aerospace, and low-altitude economy." The 2025 government work report stated, "Adding a batch of national-level advanced manufacturing clusters, with rapid development of emerging industries such as commercial aerospace, BeiDou applications, and new intelligent technologies, carrying out large-scale application demonstration actions for new technologies, new products, and new scenarios, and promoting the safe and healthy development of emerging industries such as commercial aerospace, low-altitude economy, and deep-sea technology." The emphasis on commercial aerospace continues to increaseThe "14th Five-Year Plan" also emphasizes the development of the aerospace industry. In October 2025, the State Council issued the "Suggestions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China on Formulating the 15th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development," which proposed to "cultivate and expand emerging industries and future industries, focusing on building emerging pillar industries. Implement industrial structure adjustments, promote the integrated advancement of innovative infrastructure construction, technological research and development, product iteration and upgrading, and accelerate the development of emerging industrial clusters such as new energy, new materials, aerospace, and low-altitude economy. Improve the industrial ecosystem, implement large-scale application demonstration actions for new technologies, new products, and new scenarios, and accelerate the large-scale development of emerging industries."
The National Space Administration issued the "Action Plan for Promoting High-Quality Development of Commercial Aerospace (2025-2027)," guiding the industry's development path. In November 2025, Xinhua News Agency reported that the National Space Administration issued the "Action Plan for Promoting High-Quality Development of Commercial Aerospace (2025-2027)," which clarified 22 key measures in five major areas to promote the high-quality development layout of commercial aerospace. It specifically stated, "Encourage commercial aerospace to layout large industrial chains and applications," "Focus on supporting commercial aerospace entities to develop new technologies and new products, and explore new application scenarios," and "Improve the strategic system and mechanism for commercial aerospace development, and establish a national commercial aerospace development fund." In terms of promoting industrial development, the "Action Plan" clearly states to optimize the industrial structure, encourage commercial aerospace to layout large industrial chains and applications, improve infrastructure construction, expand application services, enhance measurement and control operation capabilities, and promote high-quality development of the commercial aerospace industry. Support the expansion of the commercial ecosystem. Support commercial aerospace entities to strengthen systematic intelligent technology transformation, system development, and application services around new fields such as space resource development and utilization, space manufacturing, online maintenance and services, space environment monitoring and detection, space warehouse monitoring and early warning and mitigation, space tourism, and space biopharmaceuticals.
The establishment of the Commercial Aerospace Department marks the arrival of a dedicated regulatory agency for commercial aerospace. According to a report by Xinhua News Agency in November 2025, the National Space Administration has recently established the Commercial Aerospace Department, and related businesses are gradually being developed, marking the arrival of a dedicated regulatory agency for China's commercial aerospace industry, which will continue to promote the high-quality development of China's commercial aerospace, with the entire industrial chain expected to benefit. In recent years, China's commercial aerospace has made historic leaps under the guidance of policies, technological breakthroughs, and market-driven forces, achieving collaborative innovation across the entire industrial chain. A relevant person in charge of the National Space Administration introduced that currently, the number of commercial aerospace companies in China exceeds 600, gradually releasing the development potential of commercial aerospace while ensuring safety.
Commercial aerospace is expected to receive more financial support, helping leading enterprises actively support breakthroughs. According to a report by Caixin, on the morning of November 26, 2025, the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Finance, and other departments jointly issued relevant policies to initiate national innovation equipment enterprises; Deloitte and commercial rocket companies have officially implemented special regulations independently developed through technology innovation platforms, and these two important policies will inject strong momentum into the development of the commercial aerospace industry. 1) National innovation equipment enterprises will focus on the marine, Yangtze River Delta, and Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area economic core zones; in terms of industrial direction, they will layout in cutting-edge fields such as integrated circuits, artificial intelligence, biomanufacturing, and future energy, vigorously supporting the development of our country's chip industry, while commercial aerospace also actively promotes human scienceThe core position in the layout of the industrial and green low-carbon technology industry. 2) The introduction of special regulations for the Sci-Tech Innovation Board has created a "green channel" for commercial aerospace companies to access the capital market. This is the first time that special implementation rules have been issued for a single industry since the restart of the fifth set of listing standards for the Sci-Tech Innovation Board. Previously, this standard had clearly included support for fields such as the Ministry of Engineering, low-altitude economy, and commercial aerospace, while this regulation further focuses on the commercial rocket track, clearly defining core indicators such as the hardware structure, technological advantages, transformation of scientific research achievements, qualification certification, and commercial space of enterprises.
3.3 China is actively laying out large constellations and space computing power
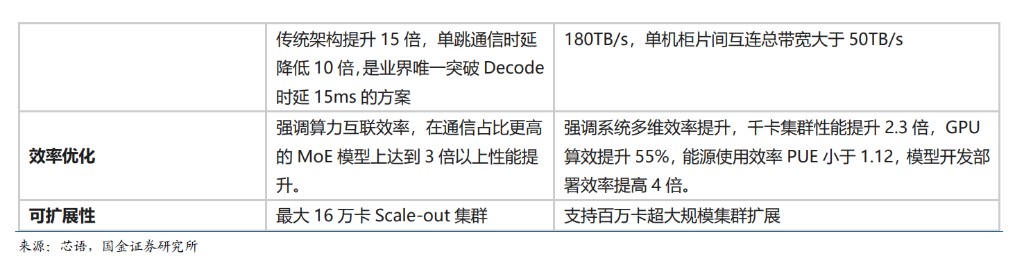
China plans multiple satellite constellations to actively seize scarce orbital resources. According to the WeChat public account of Dongfang Zhongke: 1) On April 28, 2021, China Star Network was established, marking the joint promotion and acceleration of China's space interconnection construction with resources and private capital, leading the construction of the giant low-orbit satellite project "GW" constellation plan, integrating existing satellite plans such as massive constellations and Hongyun constellation to achieve comprehensive layout of satellite networks. The GW constellation includes two sub-constellations, GW-A59 (6,080 satellites) and GW-2 (6,912 satellites). 2) China's second-largest giant low-orbit commercial satellite constellation—G60 constellation (also known as: Qianfan constellation) deployment plan aims to provide global network coverage with 1,296 satellites by 2027, and complete the networking of over 10,000 satellites by 2030, providing global users with low-latency, high-speed, and highly reliable multi-distance integrated satellite internet services. 3) On May 24, 2025, the ITU received application documents submitted by Shanghai LanJian Hongqing Technology Co., Ltd. (referred to as: Hongqing Technology), stating that the "Honghu No. 1" constellation is China's third giant low-orbit satellite constellation plan with over 10,000 satellites, following the GW constellation and G60 constellation plans. According to ITU regulations, satellite orbital resources and frequency resources are granted on a "first-come, first-served" basis. To truly possess frequency usage rights, the approved entity must complete satellite launches and signal verification within a seven-year deadline. If not completed, the resources will be forfeited.
Since 2025, the speed of China's low-orbit satellite networking has significantly accelerated, and the subsequent networking pace is expected to further increase. The Qianfan constellation will begin its first networking in August 2024, while the GW constellation will start networking at the end of 2024. Statistics show that the networking of China's two major constellations significantly accelerated in 2025. As of December 26, 2025, the GW constellation successfully launched a total of 16 groups of low-orbit satellites in 2025. We believe that due to the scarcity of orbital resources, the speed of China's satellite networking is expected to further accelerate.
In terms of space computing power, China is also actively laying out. 1) On May 14, 2025, China's first full-orbit planetary space computing satellite constellation officially entered the networking stage, which is also the inaugural launch of China's "Three-Body Computing Constellation." The "Three-Body Computing Constellation" is a large-scale space computing infrastructure on the scale of thousands of miles, and once completed, it will achieve a total computing capacity of 1,000 POPs (one hundred billion billion calculations per second)Among them, the core payload of the launched computing satellite—the onboard intelligent computer has upgraded the satellite's computing power from a lower level to P level, achieving a 10-100 times improvement; the onboard high-speed radar, as the core equipment of high-order sub-constellations and multi-satellite networks, will complete inter-satellite, satellite-ground, and intra-satellite high-speed, low-latency network transmission at hundreds of Gbps. 2) According to the implementation of IT, Beijing will launch the first computing test satellite of the supporting research and development computing constellation—"Chengguang No. 1," which has completed product development and is currently undergoing assembly testing. It is expected that within about 5 years, the first space computing center will be established. According to the plan, the space data center will be deployed in the dawn-dusk orbit at an altitude of 700 to 800 kilometers, and the construction process will be divided into three stages: "Sky Computing," "Ground Computing," and "Space-based Main Computing." The project adopts modular and standardized design, building a platform for satellite-level large spacecraft through online meetings, ultimately possessing ultra-large-scale training and inference capabilities. In terms of computing power enhancement, the plan clearly states: within the next 3 years, the constellation's space computing power will reach the level of 1000P (10 quadrillion floating-point operations per second); by 2030, computing power is expected to increase to 400,000 P, equivalent to the total computing power of all ground data centers in China, and the first space data center will be officially completed. At the same time, this center will play a core supporting role in multiple key areas such as 6G communication, autonomous driving, and weather forecasting, injecting strong momentum into technological breakthroughs and large-scale applications in related industries.
3.4 China's rocket launch bottleneck is expected to gradually break through
Currently, China's launch pace is relatively slow, with the core contradiction being insufficient launch capacity. According to reports from China National Radio, the current launch pace of China's low Earth orbit satellite constellation cannot be called large-scale networking and faces pressure from "frequency occupation and orbit maintenance"—the International Telecommunication Union stipulates that operators must launch the first satellite within 7 years of the mid-term report, launch about 10% of the constellation within 9 years, complete 50% within 12 years, and achieve 100% deployment within 14 years. The current core contradiction lies in the overall satellite launch, while rocket launch capacity is severely insufficient. The rockets responsible for launching the two major satellite constellations include the Long March 12, Long March 8A, Long March 6A, and other "national team" rockets, but these rockets also need to be used for other national space missions, leading to tight scheduling; meanwhile, the immature commercial space companies have limited available launch capacity, resulting in overall launch progress falling short of expectations.
Breakthroughs in reusable technology can significantly reduce rocket launch costs. According to 36Kr, in 2015, the Falcon 9 rocket's first stage successfully landed and was recovered for the first time, in 2016 it achieved landing recovery on a sea platform for the first time, in 2017 it achieved reusability of the rocket, and in 2019 it launched the first batch of 60 satellites into orbit. According to Economic Observer, the near-Earth orbit capacity of SpaceX's "Falcon 9" is about 22.8 tons, with a single launch quote of about $69.75 million in 2024, equivalent to about $3,000 per kilogram (approximately RMB 21,000 per kilogram), while domestic commercial rocket launch quotes are mostly between RMB 60,000 and RMB 150,000 per kilogram. The Falcon 9 can achieve recovery and reuse of the first stage rocket and fairing: the cost of a single stage rocket is about 67%The cost of rectifying the military accounts for about 10%. SpaceX has become capable of reusing the first stage of a single rocket 22 times, with total recovery costs exceeding 300 times, while the rocket cost has significantly increased. Philip Johnston, co-founder and CEO of Starcloud, stated, "We expect the cost of each rocket to be around $500, reaching the breakeven point. With the use of Starship, we anticipate even lower launch costs."
Once fully operational, the monthly price is expected to range between $10 and $150.
China's breakthroughs in reusable rocket technology are approaching, with the "national team" and the public actively competing in a positive manner. 1) On December 3, 2025, the Zhuque-3 remote—launch vehicle was launched from the Dongfeng Commercial Aerospace Innovation Experimental Zone, successfully completing its flight mission, with the rocket's second stage entering the designated orbit. Meanwhile, this mission conducted a flight verification of the vertical recovery technology for the first stage. According to flight measurement data, the first stage of the rocket experienced significant anomalies on land, failing to achieve a directed landing, and the debris was found at the edge of the recovery area. 2) On December 23, the Long March 12A remote—launch vehicle was launched from the Dongfeng Commercial Aerospace Innovation Experimental Zone, with the second stage entering the designated orbit, while the first stage failed to be successfully recovered, but the flight test mission achieved basic success. Although this mission did not achieve the planned recovery target for the first stage of the rocket, it obtained key engineering data on the rocket's real flight status, laying an important foundation for subsequent launches and reliable recovery of the stages. According to Beike Finance, there is no precedent for the first launch or recovery. Falcon 9 took 5 years from its maiden flight to successful recovery, experiencing over 20 trial-and-error explosions, while the new generation of rockets faced multiple setbacks such as engine explosions and tank ruptures before achieving orbit. We believe that with current policy support and the active competition between state-owned enterprises and the public, China's rocket launch bottleneck will be rapidly broken through.


We believe that the current aerospace industry is in a rapid development stage from 1 to 10, and the technology of reusable rockets, as an industry bottleneck, is expected to break through quickly. The global acceleration of competition in space computing opens up a broad application market for the aerospace industry, which is expected to continue to perform well in 2026.
IV. Four Symbols Three: Embodied Intelligence is Expected to Become Precise and Useful, Realizing the Foundation for Volume Growth
The "14th Five-Year Plan" proposed to "make embodied intelligence a new economic growth point." Policies continue to enhance the strategic positioning of "embodied intelligence," with the 2023 "14th Five-Year Plan for Robot Industry Development" mentioning intelligent features for the first time, and it was first included in the "Government Work Report" in 2025, with the 20th Central Committee's Fourth Plenary Session of the "15th Five-Year Plan."The plan clearly states that "intelligence will be developed into a new economic growth point," and local governments are actively responding with clear quantitative targets to accelerate industrial implementation.
➢ Beijing: It is proposed that by 2027, more than 100 key technologies will be broken through, producing no less than 10 internationally leading software and hardware products; achieving no less than 100 large-scale applications, with total production scale breaking 10,000 units first, and cultivating a trillion-level industrial cluster.
➢ Shanghai: It is proposed that by 2027, breakthroughs in core algorithms and technologies in aspects such as modeling and embodiment will reach no less than 20 items, and the scale of the core intelligent industry in our city will exceed 50 billion yuan.
➢ Shenzhen: It is proposed that by 2027, more than 10 newly cultivated enterprises with a valuation exceeding 10 billion yuan will be added, more than 20 enterprises with revenue exceeding 1 billion yuan, achieving more than 50 billion-level application scenarios, and the scale of related industries will reach over 100 billion yuan.
Tesla's Optimus V3 is nearing release, expected to be the largest cost in the development of robotic brains, with rapid improvements in the accuracy of various tasks. Musk has confirmed that "Optimus V3 will start mass production in 2026," so the release of V3 before mass production will be closer. Currently, according to Musk's public statements, "Optimus V3 will have significant improvements in hand flexibility and AI brain capabilities," and thanks to the multi-degree-of-freedom motion system and adaptive learning ability, it is expected to become the largest cost in the development of robotic brains:
In terms of hand flexibility, Musk stated, "The human hand is an extremely exquisite result of evolution. The muscles that drive the human hand are actually in the forearm, and the human hand has about 27 or 28 degrees of freedom. To make robots truly general-purpose humanoid robots, the 'hand' problem must be solved. The fundamental difficulty in building robots lies in hardware design, with the hand and forearm being the most challenging engineering aspects. If the hardware issues are resolved, software can directly utilize large-scale virtual machine robots to issue commands."
Regarding the AI brain, Musk confirmed that "V3 has already enabled the Grok voice assistant," and the integration of Grok with Optimus may allow the robot to interact more naturally with the surrounding environment and users, making Optimus more user-friendly for ordinary consumers.
The multi-degree-of-freedom motion system has over 200 degrees of freedom in the whole body, with the hand having 11-27 degrees of freedom, allowing for precise control and fine operations, such as lifting 20-pound objects or completing tasks like packing boxes, along with perception and computing systems.
Adaptive learning capabilities, for example, through end-to-end neural networks, can generate joint control sequences using only 2D camera, hand tactile, and pressure sensor data, enabling self-correction of errors in tasks such as sorting batteries.
On the model brain side, Gemini 3.0 Pro has achieved a leap in multi-modal understanding capabilities, making previously impossible tasks possible for robots in various scenarios. Gemini 3 has strong multi-modal understanding capabilities, scoring 72.7% in the ScreenShot-Pro evaluation benchmarkSignificantly ahead, it is twice that of Claude Sonnet 4.5 and two times that of GPT 5.1. The improvement in spatial reasoning capabilities allows the model to better serve autonomous driving, robotics, XR devices, and smart terminals, accelerating embodied intelligent perception. Gemini 3 Pro can predict motion trajectories, understand object relationships, and assess task progress, laying the foundation for the next generation of automation systems, and is a key step towards physical robots. In the future, the unification of "perception-decision-action": the model learns to recognize buttons on screens and operate them, while robots recognize objects in reality and complete grasping tasks, which is fundamentally interconnected. This capability can also naturally extend to understanding and controlling real devices and complex operational interfaces. We believe that in the future, robots will be able to understand various human commands and complete generalized tasks in conjunction with the scene, making what was once impossible possible, which is the foundation of true intelligent effectiveness.

From an industry perspective, Tesla's humanoid robots are expected to usher in a production milestone year, becoming the starting point for everything. At Tesla's 2025 shareholder meeting, Musk clearly stated, "We will start mass production of Optimus V3 in 2026, launch V4 in 2027, and iterate to V5 in 2028; the long-term plan is to achieve an annual production capacity of 10 million units, with the final cost reduced to $20,000." The company plans to first establish a production line for 1 million units of Optimus annually at its Fremont factory in California, and build a larger production line at the Texas Gigafactory, with an expected annual capacity of tens of millions of units. We believe that with the mass production of Optimus in 2026, combined with a leap in large-scale multimodal understanding capabilities, intelligent applications will truly begin, delivering real value in certain simple scenarios and becoming the starting point for everything.
V. Four Symbols Four: AI applications are emerging, large models/AI infrastructure/high growth/high barrier vertical software are worth paying attention to
The fundamentals of the computer industry have bottomed out and are rebounding in the second half of 2025, meeting the conditions for a rebound. According to the Wind Software Index (882250.WI), it can be seen that the software industry's revenue has bottomed out and is rebounding in the second half of 2025. In Q3 2025, the industry's operating revenue reached 176.519 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 1.61%. The revenue side is stable throughout the year, with a slow recovery; the net profit attributable to the parent company is 377 million yuan, a year-on-year increase of 244.56%, mainly benefiting from various cost reduction and efficiency enhancement measures.

5.1 Large Models: Widely Applied, Deepening into Personalization and Ecosystem Development
Large models themselves are the most representative AI applications, with global leading models achieving an ARR of tens of billions of dollars. 1) Whether it is OpenAI and Gemini, or Deepseek and Owen, large models themselves are the most representative AI applications2) Since the end of 2022, after about 3 years of development, OpenAI's ARR is expected to exceed $20 billion by the end of 2025, with plans to achieve a "digital dollar" level of revenue by 2030; Google Gemini has not directly disclosed its ARR, but its token usage has increased exponentially, reaching 1.3 trillion per month by October 2025; Anthropic Claude's ARR reached $5 billion by July 2025, having increased fivefold in the past 7 months. 3) Domestically, the usage of large models is also growing rapidly. For example, by December 2025, the daily average token usage of Baidu has exceeded 50 trillion.

In the process of using large models, users can deeply integrate them with their personal knowledge bases and workflows. 1) The use cases for large models go far beyond dialogue and search; users can leverage large models to design and build automated, intelligent workflows aimed at improving efficiency and simplifying tasks to achieve specific goals. 2) Based on daily work and life, workflows can include information collection and organization, content creation and assistance, task management and reminders, financial planning and analysis, health management, travel planning, etc. Compared to general AI, custom Agents can deeply integrate with the user's personal knowledge base and workflow, and through repeated use and feedback, the personalization and effectiveness of the Agent can be continuously improved.

Leading vendors have released various development tools to facilitate the easier and deeper deployment of foundational models. 1) OpenAI: In October 2025, OpenAI developers will hold a conference to release the AgentKit toolkit, which includes many modules that can help developers design workflows more efficiently. For example, through the Agent Builder module, developers can quickly build Agents in a visual and intuitive way without starting from code, simply by adding and configuring a series of nodes. OpenAI researchers demonstrated on-site how to build an Agent for their developers' daily access site using AgentKit in just 8 minutes. 2) Tencent: WeChat will eventually launch an AI intelligent body that allows users to complete multiple tasks within WeChat, capable of understanding users' needs, intentions, and interests. It is stated that WeChat has a powerful communication and social ecosystem, as well as shopping and payment scenarios, making it almost an ideal assistant for users. However, Liu Hanping also believes that this vision is still in a "very early stage"; currently, WeChat is introducing Yuanbao capabilities in multiple locations, including using AI to enhance search, etc. At the same time, Tencent is also developing intelligent capabilities in vertical fields, which will gradually be opened and integrated in the future to create the ideal blueprint for the WeChat intelligent body
5.2 AI Infra: Obtaining certain returns from selling shovels, directly laying the foundation for application quality
AI Infra does not directly produce models and applications, but provides the basic "water, electricity, and coal," directly establishing the "cost" and "ceiling" of AI. 1) Computing power scheduling: Similar to traffic control, it allocates massive computing tasks to tens of thousands of processors (GPU/TPU) and handles node failures to ensure uninterrupted training. 2) Data throughput: During training, massive amounts of data need to be "fed" to the GPU as much as possible, preventing the GPU from waiting for data (IO Wait), requiring high-performance storage and networks; during inference, high concurrent data influx requires maximizing CPU/GPU computing efficiency and reducing user latency. 3) Model training and inference support: Providing environments and tools to enable models to learn quickly and be available quickly when users utilize them. 4) Resource abstraction and virtualization: Developers do not need to worry about what kind of GPU is underlying, as they can directly call computing power through the software layer.
Databricks: "Lakehouse" global big data leader, AI revenue has reached $1 billion.
- Databricks was founded in 2013 and primarily provides a unified data and AI platform service, helping enterprises integrate and process large-scale data for data engineering, data science, machine learning, and AI applications, and can also provide data services for enterprises in e-commerce, finance, healthcare, and other fields. The company is the pioneer of the "lakehouse" database architecture, a representative enterprise in the field of data intelligence, and an important data infrastructure provider in the AI era. According to self-reported data, as of December 2025, over 60% of Fortune 500 companies have adopted Databricks' data intelligence platform to manage data and integrate it with AI.
- With the comprehensive penetration of AI technology, the "lakehouse" model is becoming the core selection for data infrastructure. In response to the demand for multi-modal complex data throughout the AI lifecycle, this architecture not only achieves unified management and real-time processing but also utilizes cloud-native elastic scaling mechanisms to achieve efficiency gains. Notably, it has also undergone underlying optimizations for AI scenarios, such as building vector search capabilities and optimizing development ecosystems like Pytorch, thereby streamlining the complex processes from data preprocessing to model application.
- On December 16, Databricks announced the completion of over $4 billion in financing, with a post-investment valuation of $134 billion. In terms of operational data, the company disclosed that its annualized revenue for the third quarter exceeded $4.8 billion, a year-on-year increase of over 55%; at the same time, its annualized revenue scale for AI-related products and data warehouse business both exceeded $1 billion, achieving free cash flow over the past 12 months

Snowflake: A versatile data cloud platform, Cortex is expected to become a pillar for enterprise AI development.
Snowflake was established 13 years ago and has built a complete data and AI platform based on public cloud. It is dedicated to helping customers handle various types of data, supports multiple languages for development and data modeling, and provides applications in data engineering, data analysis, AI, and data sharing for business users. As of November 2025, Snowflake has over 12,000 enterprise-level customers worldwide, with more than 50% of customers using its AI features and products.
Snowpark: Allows developers to process data directly within Snowflake using languages like Python and Java instead of SQL. This is key for machine learning.
Snowflake Cortex: A native AI and machine learning suite built directly on the Snowflake platform. It enables users to run advanced AI models using Snowflake data without migrating data or configuring separate infrastructure.
In FY2026Q3, Snowflake achieved total revenue of $1.213 billion, with a net loss of $294 million. Among them, AI business annualized revenue exceeded $100 million, about a quarter ahead of the original plan, mainly due to innovation speed, efficient cross-department collaboration, and early adoption by numerous benchmark customers.

5.3 High-growth scenario applications: Advertising marketing, dynamic comics, healthcare, etc., are expected to run the flywheel
We believe that large models have stronger semantic understanding, data analysis, and multimodal processing capabilities compared to previous generations of AI. In some scenarios, they have already shown better implementation potential, and the high growth trend is quite significant.
Advertising marketing has become one of the most representative scenarios for the commercialization of AIGC. 1) Thanks to the high-frequency and massive business characteristics of this scenario, the "data flywheel" effect based on AIGC has successfully run through, achieving a positive cycle of algorithm optimization and delivery effectiveness. Unlike simple cost reduction, AIGC can directly bring quantifiable revenue increments and ROI (return on investment) improvements to advertisers through precise delivery and automated material generation, effectively stimulating downstream customers' willingness to pay and promoting this scenario to be the first to achieve the leap from technology validation to large-scale application. 2) Taking Applovin as an example, its revenue profits have grown rapidly in recent years. Its business includes three main areas: app games, advertising platforms, and underlying algorithm infrastructure, all of which can drive each other to rotate the business flywheel
The release of multimodal technology dividends has made dynamic comics a "hit." 1) With the convergence and breakthroughs in multimodal large model technology paths by 2025, the visual expressiveness of dynamic comics has achieved a qualitative leap. On the demand side, its narrative rhythm is compact, and emotional density is high, accurately integrating current user entertainment preferences during fragmented time; on the supply side, compared to traditional animation or live-action short dramas, the production cycle of dynamic comics empowered by AI has been significantly shortened, offering notable advantages in low cost and mass production. The technological leap combined with supply-demand adaptation is accelerating this channel's transition from the fringe to the mainstream. 2) According to statistics from Douyin Engine and Volcano Engine, in the first half of 2025, the commercialization of the comic drama market is experiencing rapid growth, with Douyin's comic drama paid natural flow: from 0 in the first half of 2024, it surged to over 3 million per day in the second quarter of 2025 and over 10 million per day in August 2025; Douyin's comic drama commercialization traffic: from 10,000 per day in the second half of 2024, gradually rising to 200,000 per day during the Spring Festival, 800,000 per day in the second quarter of 2025, and peaking at 4 million per day in August 2025.

Medical AI capabilities are undergoing a comprehensive leap and are expected to become the next high-growth scenario. 1) This scenario has a solid foundation of high-quality private data accumulation and exquisite medical expert resources for model training. By combining expert annotations (RLHF) with existing scene positioning advantages, AIGC can effectively integrate fragmented information, achieving a complete business loop from "data elements" to "clinical decision support." This deep integration not only meets the high demands for professionalism and accuracy in the medical field but also helps vendors with core data assets build more complex competitive advantages. 2) From case studies, as of December 16, 2025, Ant Group's Aifu ranked third on the Apple App Store for the Xingjia platform, with monthly active users exceeding 15 million; Meinian Health may become a core beneficiary by leveraging nearly 300 million medical-grade health check data accumulations, covering nearly 600 offline service networks nationwide, and a mature AI product matrix.
5.4 High-barrier application categories: possessing data and workflow moats, providing more significant value to customers
The development of large models will accelerate the commercialization and elimination of "simple applications"; however, for applications with deep industry know-how, proprietary data assets, complex process integration capabilities, and strict compliance qualifications, large models will not only not be a threat but will instead become a key tool to consolidate their core advantages"Simple" applications generally possess the following characteristics: 1) Dependence on public knowledge: Core input and output are based on commonly available internet corpus and its information; 2) Low verification threshold: The quality and correctness of results can be quickly assessed (e.g., code unit testing); 3) Weak responsibility risk: High error rates are easily manageable, and rollback costs are low (e.g., image generation, article editing); 4) Low system coupling: Tasks are singular and do not involve cross-system collaboration or complex permissions and auditing processes.
In contrast, deep-layer applications have four major barriers driven by big data business:
- Deep industry know-how: Specific industries rely on tacit experience, situational judgment, and immature standards, making it difficult for general large models to create extensive virtualized and hierarchical domain knowledge. Therefore, companies that can convert rich domain business logic into specialized models or agents will build more significant competitive barriers with higher accuracy and reliability through this general solution.
- Proprietary data assets: As infrastructure capabilities become widespread, the competitive focus will shift from the model layer to the data layer. Having unique, high-quality, and hard-to-obtain closed-loop data through public channels is the core differentiating advantage. In this scenario, large models serve merely as amplifiers of data value, with data owners occupying a dominant position in the value chain.
- Complex process integration: The value of modern enterprise software lies in the deep orchestration of cross-departmental, multi-step business processes (e.g., ERP systems integrating finance, HR, and approval flows). This deep embedding in workflows creates high customer stickiness and replacement costs. Large models struggle to independently execute highly coupled and moderately complex tasks and are more likely to be integrated into existing systems to enhance efficiency.
- Qualification and compliance barriers: In the field of enhanced management, business operations depend on clear trust entities, qualification permissions, and compliance systems. Although models can assist in production, the ultimate legal responsibility and result endorsement must be borne by qualified entities. This rigid constraint determines the irreplaceable position of such companies in the industry chain and their higher bargaining power.
These factors also determine that application companies can capture greater value in collaboration with foundational models.
Palantir: Military business as a foundation, showcasing Alpha in complex scenarios
- Palantir was founded in 2003, headquartered in Denver, Colorado, USA, and began actual operations in 2004, focusing on providing big data integration, visualization, and analysis platforms to help organizations derive value from vast and complex data. With its powerful data mining and analysis capabilities, Palantir has become a core supplier of big data software for U.S. military agencies and has rapidly expanded into high-demand areas through its development of "quality civilian isolation" and tracking strategies. In the commercial sector, it helps clients build data infrastructure through deep collaboration, utilizing data mining and analysis to achieve business success, with clients including JP Morgan, Merck Group, Airbus, and Chrysler.
According to research from the Broadcasting and Telecommunications Research Institute, unlike many SaaS companies, Palantir adopts a deeply customized approach to collaborate with clients, with each project potentially requiring months or even years. It not only provides software platforms but also deeply engages in clients' data integration and decision-making processes, forming a "software + consulting" hybrid service modelThis model enables Palantir to solve the most complex data problems for clients. Although it limits the rapid growth of the customer base, it also establishes high customer stickiness and switching costs.
The products include four categories: 1) Palantir Gotham for government and intelligence agencies; 2) Palantir Foundry for enterprises; 3) Apollo platform specifically supporting Gotham and Foundry; 4) AIP platform based on Palantir's machine learning technology and large-scale capabilities. Among them, the AIP platform focuses on providing advanced data integration, analysis, and intelligent decision support solutions, offering powerful capabilities of large language models and advanced artificial intelligence technology; whether on machine systems or technical edge devices, AIP can achieve responsible AI solutions in private networks. Effective and secure deployment can efficiently build AI applications, continuously improve the functionality of AI-driven workflows, and provide Ontology SDK for rapid integration with enterprise operations.

VI. 3D Printing: When Innovation Meets Physical Bottlenecks, 3D Printing Begins
The Chinese 3D printing market is returning to rapid growth, with the global market size expected to exceed USD 11.45 billion by 2034. The overall investment and financing amount in the Chinese 3D printing sector is rapidly increasing, with the total industry investment and financing expected to reach CNY 8.4 billion in 2025, setting a historical high and a year-on-year growth of 115.4%, reversing the decline seen in 2024. Driven by demand in aerospace, liquid cooling, 3C, and automotive sectors, the global 3D printing market is set to experience rapid growth. According to WOHLERS statistics, the global 3D printing market size will reach USD 21.9 billion in 2024, and it is expected to grow steadily towards USD 100 billion at an annual growth rate of 18% over the next decade, with an expected breakthrough of USD 11.45 billion by 2034.

We believe that as industries such as AI, aerospace, 3C, robotics, and automotive continue to break through innovation boundaries, traditional manufacturing processes are nearing their limits and are unable to meet practical needs such as heat dissipation and lightweighting. There is an urgent need for 3D printing technology to break through traditional limits, and the explosion of multidimensional demands is expected to accelerate industry development.
The AI boom, coupled with 3D printing, empowers microchannel solutions to address heat dissipation pain points. With the explosive growth of power density in AI chips, there is an urgent demand for microchannel liquid cooling solutions with extremely high heat exchange efficiency. However, traditional processes such as milling, CNC, and welding are limited by manufacturing principles when creating microchannels (with large aspect ratios, complex geometric structures, and diameters less than 1mm), making it difficult to achieve finely detailed flow channel formation. Additionally, the welding process introduces thermal resistance and leakage risks, making it challenging to match the innovation pace of AI chips, thus necessitating the assistance of 3D printing to break through manufacturing limits3D printing has completely liberated the constraints of channel design. Its integrated molding capability, which does not require molds or welding, can directly manufacture complex channels such as topology optimization and bionic vein structures that traditional processes cannot achieve, significantly increasing the heat exchange surface area and optimizing fluid dynamics performance. At the same time, through micron-level precision manufacturing, it can fundamentally eliminate the thermal resistance and leakage risks caused by welding, enhance structural strength, and perfectly meet the rigid demand for extreme heat dissipation performance of the new generation of AI chips.

3D printing reduces the production costs of rocket engines and reshapes the aerospace era. The aerospace field has extremely high requirements for the strength, lightweight, and complex structure integration of components, which naturally couples with the characteristics of 3D printing. Taking rocket engines as an example, their manufacturing costs account for up to 50% of the total cost of the rocket. To pursue extreme performance and cost-effectiveness, 3D printing is widely used in this field:
- Tianbing Technology's Tianlong II uses a 3D printed high-pressure regenerative engine, with nearly 90% of its components completed through additive manufacturing. Compared to traditional processes, the manufacturing cycle of this engine is shortened by 70%-80%, with costs and weight reduced by 40%-50%.
- Xinghe Power's "Cangqiong" liquid oxygen/kerosene engine employs 3D printing technology, achieving a 4:1 thrust-to-weight ratio and 50 reuse cycles. Fei'er Kang Technology collaborated with Xinghe Power to utilize Huashu High-tech's metal 3D printing solutions, completing the delivery of over 30 rocket engine parts within 4 months.
- Interstellar Glory's Hyperbola II verification rocket completed China's first full-size vertical takeoff and landing and reuse flight test of a liquid rocket. Plittech developed several key engine components for it, effectively helping to shorten the production cycle and save costs.
- We believe that 3D printing in the aerospace field has broken through the limits of traditional processes, providing integrated complex structure production capabilities, faster R&D pace, and better strength and lightweight performance at lower costs. As a necessary production link, it is expected to usher in a definitive demand explosion with the rapid emergence of commercial spaceflight.

3D printing solves the dual constraints of intelligent lightweight and heat dissipation through topology optimization.
In terms of lightweighting, 3D printing, with its ability to form complex geometric shapes, can manufacture high-strength and hollow skeletal and limb components through topology optimization design and lattice structures. While significantly reducing the weight of robots and enhancing their mobility and endurance, it also notably reduces the number of components and assembly difficulty through integrated molding.
In terms of heat management, facing the narrow internal space of humanoid robot joints and the heat accumulation caused by motor load operation, traditional cooling methods often struggle to be effective. However, 3D printing can directly integrate heat management functions into structural design, greatly increasing the effective heat dissipation surface and expanding heat exchange efficiency by constructing complex integrated thermal conduction systems and optimizing internal heat conduction pathsEffectively addressed the risk of thermal accumulation failure under high integration, laying a physical foundation for intelligent high dynamic performance iteration.
In the era of edge AI, 3D printing can enhance thermal management and customization. As AI is widely implemented in mobile devices such as smartphones and AIPC, the surge in heat flow density caused by the instantaneous high computing power of chips conflicts with the spatial limitations of lightweight devices. 3D printing technology can produce ultra-thin heat spreaders that adapt to the space of irregular soft hoses, which cannot be achieved by traditional stamping or molding processes. By constructing complex internal three-dimensional capillary structures, it significantly improves passive heat dissipation efficiency, ensuring the stable operation of edge AI. On the other hand, in response to the trend of high-strength alloy structures for the lightweight and flexible components of foldable screens, 3D printing has largely addressed the issues of low yield rates, significant tool wear, and difficulty in machining complex internal cavities associated with traditional CNC processing of titanium alloy materials. It has achieved integrated forming and topological weight reduction of lightweight steel belt components, providing valuable space for battery release while meeting the folding life of hundreds of thousands of times, becoming the preferred solution for high-end 3C products to balance lightweight and durability.

3D printing helps the automotive industry break through the lightweight bottleneck. In the field of integrated lightweight vehicle structure, traditional stamping and casting processes are limited by the logic of separate manufacturing, requiring welding and assembly of multiple components, which poses risks of fatigue failure at connection points. 3D printing technology can utilize topology optimization algorithms to design key components such as chassis subframes and control arms into biomimetic hollow or lattice structures and achieve integrated forming, significantly reducing weight while avoiding strength degradation caused by multi-component welding. At the same time, in response to the growing demand for personalization in high-end models, this technology completely eliminates the dependence on expensive molds for the manufacturing of interior and exterior parts, enabling the direct production of seat mid-layers with complex lattice structures, specially textured dashboards, and irregular vehicle body shells. This not only significantly shortens the R&D trial production cycle but also meets the dual customization needs of functionality and aesthetics for smart cockpits through low-cost small-batch production models.

VII. Financial IT: Global capital active in the interest rate cut cycle, cross-border payments reconstructing the financial ecosystem
The interest rate cut cycle opens up valuation elasticity for global assets, and the performance of financial IT is expected to recover. Global liquidity is reaching a turning point, with the 2025 easing cycle combined with expectations of interest rate cuts in 2026, which is expected to improve the valuation environment for risk assets. According to Bank of America statistics, the amount of interest rate cuts by global central banks in the past two years has exceeded that during the 2008 financial crisis. Although the current neutral interest rate remains high, institutions predict that the Federal Reserve still has a 100 basis point room for rate cuts in the next 12-18 months, with the neutral interest rate expected to return to the range of 3%-3.25%. More critically, the marginal change is that the Federal Reserve's meeting minutes suggest that quantitative strategies will end in December, and even the possibility of focusing on quantitative easing in 2026 to counter employment pressure cannot be ruled outWe believe that substantial improvements in liquidity will effectively reduce funding costs and boost asset prices.
The trading activity in the capital markets is expected to rebound, benefiting the performance recovery of trading systems and related IT service providers.

The "14th Five-Year Plan" clearly outlines the high-quality development of the capital markets, ushering in a new wave of construction for capital market IT. On October 28, 2025, Li Chao, Vice Chairman of the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), stated at a ceremony related to the Sci-Tech Innovation Board that the CSRC will expedite the planning of strategic tasks for the capital markets during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period, focusing on the three pillars of "risk prevention, strengthened regulation, and promotion of high-quality development." Current policies emphasize deepening comprehensive reforms in investment and financing to continuously enhance the inclusiveness and adaptability of the capital markets, serving the goal of building a strong financial nation. We believe that with the new round of capital market reforms, the capital market IT sector is expected to welcome a new wave of systematic construction.
The scale of cross-border payments is steadily growing, and the global regulatory framework is evolving rapidly. The scale of cross-border payments continues to increase, from USD 141.1 trillion in 2020 to USD 194.6 trillion in 2024, with B2B business growth stabilizing. Benefiting from the expansion of e-commerce and digital services, cross-border payments involving individuals have a compound growth rate exceeding 30%, achieving rapid growth. The global regulatory framework is accelerating its evolution, with increasingly stringent compliance requirements for anti-money laundering (AML), combating the financing of terrorism (CFT), and customer identity verification (KYC). The regulatory system is transitioning to modular and real-time approaches. The coverage has expanded to include traditional cross-border payments, digital assets, and various payment forms involving cryptocurrencies; regulatory agencies are also actively introducing real-time risk control and regulatory technology tools to strengthen the identification and management capabilities of dynamic risks.

The digital renminbi has been upgraded again, further supporting the construction of a strong financial nation and promoting the internationalization of the renminbi. On January 1, 2026, the People's Bank of China issued the "Action Plan for Further Strengthening the Management and Service System of Digital Renminbi and Related Financial Infrastructure Construction," which will officially launch the new generation of digital renminbi measurement framework, management system, operational mechanism, and ecological system. The purpose of this round of digital renminbi upgrades, we believe, is mainly to: 1) implement the requirements of the "14th Five-Year Plan" to "accelerate the construction of a strong financial nation" and "steadily develop the digital renminbi"; 2) respond to global challenges posed by virtual assets/stablecoins, actively embrace blockchain and smart contract technology, and improve cross-border payment efficiency. From the details of the action plan, the three core changes are:
➢ New interest-bearing income. The digital renminbi before the upgrade was essentially "digital cash," cash in hand rather than deposits in banks, which could not generate interest income. The upgraded digital renminbi is essentially "digital deposits," and banks are required to pay interest on the digital renminbi in users' wallets, which is conducive to incentivizing users' willingness to use it;At the same time, as "digital deposits," they are protected by deposit insurance, providing a higher level of security.
➢ Strengthen smart contract functions. The upgrade of smart contract capabilities provides digital service providers with a richer "arsenal," conducive to innovating supply chain finance, green finance, prepaid fund management, targeted subsidies, and other services.
➢ Optimize cross-border experience. The upgraded digital renminbi will optimize the cross-border payment experience. For example, Chinese tourists traveling in Laos can directly scan to pay using the digital renminbi App without the need to exchange foreign currency, enhancing the experience for both Chinese tourists and Laotian merchants.
We believe that in the context of global payment innovation, the digital renminbi has been endowed with new connotations. Domestically, it attracts more users by offering interest on digital deposits, while internationally, it facilitates cross-border payments, which is expected to further promote the steady and long-term internationalization of the renminbi.

8. Intelligent Driving: L2 Strong Standards Implemented, L3 Year, Robotaxi Single Vehicle UE Turns Positive
<L2 Assisted Driving: The AEBS system becomes a driving mandatory national standard, and the "China L2 Strong Standard" draft for comments has been released.
On February 28, 2025, the "Technical Requirements and Testing Methods for Automatic Emergency Braking Systems for Light Vehicles" was completed and entered the public comment phase on April 30. This standard will replace the current national standard GB/T39901-2021 "Performance Requirements and Testing Methods for Passenger Car Automatic Emergency Braking Systems (AEBS)," upgrading from a "recommended national standard" to a "mandatory national standard."
Compared to the current national standard, the new national standard requires comprehensive upgrades to AEBS in terms of coverage, activation speed, and false detection. 1) The new national standard expands the coverage from M1 class passenger vehicles to N1 class light cargo vehicles; 2) The activation speed range for AEBS systems in M1/N1 class vehicles changes from above 15 km/h to 10-80 km/h/10-60 km/h, while clearly defining the activation speed range for effective recognition of pedestrians and two-wheeled vehicles as 20 km/h-60 km/h; 3) The testing front end includes complex scenarios such as special vehicles and bicycles, increasing the difficulty of false detection within the lane, with the required test result rate reduced from 40% to 10-20%.

Globally, Europe, the United States, and Japan have all passed relevant regulations requiring varying degrees of mandatory installation of AEBS systems. 1) In April 2024, the United States released FMVSS127, requiring that all new light vehicles produced after September 1, 2029, must be equipped with AEBS systems that meet this standard (currently, AEB systems are still recommended technologies, and NHTSA's new car assessment program has included AEBS in testing since 2018)2) In April 2021, the European Union released UNR152, requiring that new vehicle models entering the EU market from July 6, 2022, must be equipped with AEBS functions that comply with UN-R152 regulations. 3) At the end of 2020, Japan announced that new models must be equipped with AEBS systems and comply with UNR152 starting from November 2021 for domestic new models and from June 2024 for imported new models; for approved models, domestic new models must be equipped with AEBS systems and comply with UNR152 starting from December 2025, and imported new cars from June 2026.

The AEBS system consists of three main modules: perception layer (sensors), decision layer (algorithms/chips), and execution layer (brake control). The core function is to monitor the front environment in real-time through sensors, triggering an audible and visual alarm and an emergency braking response mechanism when it determines that the speed risk exceeds the threshold and the driver has not taken braking measures. In terms of technical routes, the current AEBS sensor solutions mainly involve different combinations of lidar, millimeter-wave radar, and cameras. With the new targets raising requirements for lidar speed range and false detection and missed detection rates, lidar has significant advantages.
The new targets require that the AEBS system for M1 class vehicles be activated at speeds of at least 10 km/h to 80 km/h, with the activation speed range for M1 class vehicles being 20 km/h to 60 km/h, and it is required that the absolute value of the vehicle's deceleration after emergency braking be no less than 5.0 m/s². Compared to the current target requirement of a minimum triggering speed of 15 km/h, the activation speed range has been significantly expanded. In practical applications, the industry is also continuously pursuing higher AEBS production speeds. Huawei's new M7 has currently upgraded to a production speed of 120 km/h, while Li Auto's LG can achieve a production speed of 120 km/h when facing an accident vehicle at night.
The expansion of the AEBS activation speed range actually imposes higher requirements on the sensor detection distance. At a speed of 5.0 m/s², a vehicle traveling at 80 km/h requires at least about 73 meters of braking distance, while at a speed of 130 km/h, this distance extends to 169 meters.

According to disclosures from Hesai's WeChat public account, compared to vehicles without lidar, those equipped with lidar have an approximately 50% significant increase in AEBS speed limits: 1) In the absence of lidar, the AEBS speed limit is about 85 km/h, which increases to 140 km/h when equipped with lidar; 2) In nighttime driving conditions, the AEBS speed limit without lidar is about 80 km/h, which increases to 120 km/h when equipped with lidarAt the same time, the new targets add identification requirements for pedestrians and two-wheeled vehicles, with the testing requirements for the experimental end reduced from 40% to 10-20%, and the accuracy requirements for sensors further increased. In pure vision solutions, cameras, as visual tools simulating human eyes, significantly reduce performance under complex lighting conditions such as strong light and nighttime. The average perception accuracy of a target chip supporting nighttime fusion with LiDAR is three times that of pure vision. The accuracy of millimeter-wave radar significantly decreases with the increase in detection distance; the 3G and 4D millimeter-wave radar equipped in vehicles can only recognize pedestrians at a distance of 100m. Currently, the market's 4D millimeter-wave radar outputs over 1,000 points per frame, while mainstream 128-level LiDAR can output up to hundreds of thousands of points per frame, showing a significant difference in resolution.
LiDAR can maintain tailwater-level accuracy at a detection distance of 200m. Taking the ultra-long-distance digital LiDAR EM4 of the tracking system as an example, it supports a maximum measurement distance of 600 meters, allowing for a decision-making and response time increase of up to 70%, which can significantly enhance the speed range covered by the AEBS system while improving safety.
The new targets are stricter on mobile control, and millimeter-wave radar must quickly meet the requirements. The new targets have increased the requirements for vehicle targets turning right during the following process, vehicles and pedestrians in reverse motion, the motion trajectory of stationary bicycles in the opposite direction, and the thickness of the road iron plate for lane error testing has increased from 10mm to 25mm.
3D millimeter-wave radar compresses objects ahead into a two-dimensional plane, making it unable to determine object contours and lacking height information recognition capability. Iron plates in the lane can easily be misidentified as obstacle targets. Automatic bicycles on the lane, marked navigation axes, and suspension devices or locators form measurements, using the former's millimeter-wave triggering error matching, causing severe "black-to-black" situations, even leading to rear-end collisions. LiDAR, on the other hand, reconstructs the environment in three dimensions through point cloud maps, allowing for the identification of the aforementioned obstacles without prior training, enhancing the vehicle's perception ability in complex scenarios and reducing false detection rates.
4D millimeter-wave radar has increased vertical angle detection, providing height information, but the resolution still has a significant gap compared to LiDAR. Currently, the overall price of 4D millimeter-wave radar is around a thousand yuan, and compared to LiDAR, which has already entered the $200 era, the cost advantage is not obvious. We believe that in actual production vehicles, the application of 4D millimeter-wave radar is limited, having missed the window period for installation.

On September 17, 2025, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology publicly solicited opinions on the mandatory national standard "Safety Requirements for Intelligent Connected Vehicles Combination Driving Assistance Systems." The standard sets comprehensive safety technical requirements for different functions such as single-lane, multi-lane, and navigation assistance. Based on the characteristics of road traffic in China, the standard constructs test scenarios including traffic environments such as road intersections, construction areas, roundabouts, and tunnels; to ensure that all capabilities declared by the system are fully verified, it requires passing field tests, road tests, and document verification to confirm that the system meets relevant safety requirements
L3 Conditional Autonomous Driving: "Takeover Buffer Period + Responsibility Transfer," the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) announces the first batch of L3 access permits. In December 2025, the MIIT officially announced the first batch of L3 conditional autonomous driving vehicle access permits in China. Two models, adapted for urban congestion and highway segments, will conduct road trials in designated areas of Beijing and Chongqing, marking a key step in the commercialization of L3 autonomous driving in China from the testing phase.
Compared to L2 assisted driving, L3 autonomous driving allows drivers to take their hands and eyes off the steering wheel and road, with collision responsibility potentially transferred to the manufacturer. Currently, there are mature practices overseas. Mercedes' L3 flagship models have been deployed in California, Nevada, and Germany, and it is expected that the UK will also see L3 vehicles on the road by 2026.
The L3 system needs to operate without driver intervention and requires more meticulous safety redundancy design. The United Nations "Automated Driving Regulation R157" clearly states that L3 systems must provide a 10-second takeover buffer period. The Mercedes L3 model DRIVE PILOT system can be activated at speeds of up to 40 miles per hour (approximately 64.4 kilometers per hour), setting a 10-second response takeover time. If the driver does not take over within 10 seconds, an emergency braking procedure will be initiated. This goal requires a detection distance of over 200 meters, leveraging the long-range perception capabilities of high-performance lidar. The DRIVE PILOT system adds a lidar, a wheel camera, and a rearview camera to the Mercedes L2 autonomous driving system, along with V2X modules, centimeter-level high-precision positioning modules, and high-definition maps.
The key difference between L2 and L3 levels lies in the transfer of responsibility. Mercedes promises that during the operation of DRIVE PILOT, if a vehicle safety accident occurs, the owner will not be held responsible in principle, and the manufacturer will bear all responsibility. Therefore, we believe that manufacturers are more focused on improving the safety of L3 level autonomous driving to ensure that liability costs do not exceed the potential benefits of deploying L3 systems, with high-performance lidar being indispensable.

Domestic automakers are accelerating the implementation of L3 autonomous driving. 1) In terms of policy, the introduction of regulations such as the "Beijing Autonomous Driving Vehicle Regulations," "Wuhan Intelligent Connected Vehicle Development Promotion Regulations," and "Shenzhen Special Economic Zone Intelligent Connected Vehicle Management Regulations" has stipulated the road processes, accident responsibilities, and related implementations for L3 autonomous driving vehicles, promoting the commercialization of L3 autonomous driving. 2) In terms of technology, lidar environmental perception is becoming increasingly precise, with safety redundancy reaching a high level, and the high-cost bottleneck that previously restricted the popularization of L3 is gradually being brokenIn the first half of this year, domestic car manufacturers have intensively announced their progress in L3, with L3 architecture models all equipped with multiple LiDARs. In April 2025, Huawei released the new generation ADS 4.0 intelligent driving assistance system, supporting high-speed L3 autonomous driving, making it the first commercial solution for high-speed L3 in China. The same-class M9 and single-series S800 based on the ADS 4.0 system are designed according to the L3 intelligent driving architecture and are equipped with 4 LiDARs. On March 3, 2025, Geely launched the Qianli Haohan safety high-level intelligent driving system, with the Qianli Haohan H9 serving as an L3 solution capable of mass production, equipped with 5 LiDARs.
Regarding the issue of L3 responsibility transfer, domestic car manufacturers have proposed intelligent driving solutions. Huawei has introduced the Smart Driving Worry-Free Service Rights (trial), covering scenarios such as intelligent parking assistance, valet parking assistance, remote parking assistance, lane cruising assistance, and intelligent navigation assistance, with a duration of 12 months from the activation of rights, and a maximum coverage limit of 5 million yuan. XPeng has launched the Intelligent Assisted Driving Peace of Mind Service, the first of its kind to cover the entire vehicle series and all scenarios, supporting five major insurance companies, with no limit on the number of claims, and is the only insurance plan in the industry that remains effective within 5 seconds after NGP exit.



L4 Autonomous Driving: Pony.ai's Robotaxi UE model has leveled up, with mainstream manufacturers in China and the U.S. making rapid progress. L4 is highly automated driving, requiring vehicles to operate independently and safely in specific scenarios without human driver intervention, handling all emergencies. Currently, both China and the U.S. have launched Robotaxi commercial operations in multiple cities, including Wuhan, Beijing, Shanghai, Phoenix, and San Francisco. Robotaxi demands higher environmental perception and safety redundancy capabilities, and currently, mainstream Robotaxi models adopt perception solutions that integrate LiDAR, with each vehicle equipped with 7-10 LiDARs (Waymo uses a 4 LiDAR mechanical surround solution).
By the end of the year, Pony.ai was the first to achieve city-level single-vehicle profitability characteristics in Guangzhou. At a media communication meeting on December 16, Pony.ai co-founder and CFO Wang Haojun disclosed that the average daily orders for Robotaxi in the Guangzhou area have reached 23 orders per vehicle, with average daily revenue reaching 299 yuan per vehicle (after discounts and refunds), a level that supports the Guangzhou fleet in achieving single-vehicle revenue balance in November, establishing a verifiable single-vehicle profitability modelXiaoma Zhixing's seventh-generation Robotaxi will begin fully unmanned commercial operations in Beijing, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen starting in November. The seventh-generation model is the main support for the rapid expansion of the fleet. The biggest issue with the previous fifth and sixth-generation models was their "high cost," with each vehicle costing "tens of thousands." Therefore, the more vehicles deployed, the greater the losses. However, the cost of autonomous driving conditions for the seventh-generation vehicle has decreased by over 70%, and costs are expected to drop another 20% next year compared to this year.


This year has seen the steepest growth for Hongmeng Zhixing, with five major brands achieving nearly full market high-price coverage. Hongmeng Zhixing has covered the price range of 150,000 to over 1 million yuan through its five major brands, with different market divisions starting from the end of 2025:
- Aito: Sales powerhouse, with the all-new Aito M7 delivering over 40,000 units in just 68 days since its launch, ranking first in the market for vehicles priced above 300,000 yuan; the Aito M8 has accumulated over 130,000 deliveries in 7 months, making it the delivery champion in the market for vehicles priced above 400,000 yuan; the Aito M9 delivered over 7,500 units last month, maintaining its position as the cumulative delivery leader in the market for vehicles priced above 500,000 yuan.
- Shangjie: Positioned for the entry-level market, with over 10,000 units delivered in November alone.
- Zhijie: Targeting young consumers, with monthly deliveries exceeding 10,000 units for two consecutive months.
- Xiangjie: The Xiangjie S9 series has become the sales champion for luxury electric sedans priced at 300,000 yuan.
- Zunjie: The Zunjie S800 has ranked first in luxury sedan sales for three consecutive months in the market priced above 700,000 yuan.
In terms of overall sales scale, Hongmeng Zhixing achieved its first "1 million" cumulative deliveries in 43 months. Based on the current growth rate, Richard Yu predicts that the delivery cycle for the second 1 million vehicles will be shortened to about 10 months.
In the fourth quarter of this year, due to the nationwide withdrawal of various subsidy policies, the growth pressure in the automotive market is greater than in previous years, but Hongmeng Zhixing still maintains sales growth. As of December 29 at 14:00, Hongmeng Zhixing's sales for this month have reached 83,241 units, surpassing last month's 81,864 units, setting a new historical monthly sales record and ending the year strongly.

Risk Warning and Disclaimer
The market has risks, and investment requires caution. This article does not constitute personal investment advice and does not take into account the specific investment goals, financial situation, or needs of individual users. Users should consider whether any opinions, views, or conclusions in this article are suitable for their specific circumstances. Investment based on this is at one's own risk

