
The reserves of the U.S. banking system have fallen for eight consecutive times, dropping below $3 trillion. The Federal Reserve's balance sheet reduction may be approaching a turning point

The reserves of the U.S. banking system have declined for eight consecutive weeks, falling below $3 trillion for the first time, raising market concerns about whether the Federal Reserve will end its balance sheet reduction early. According to Federal Reserve data, as of October 1, reserves decreased by $20.1 billion to $2.98 trillion, marking the lowest level this year. The decline in reserves is related to the Treasury's increased borrowing, which has affected market liquidity. Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell stated that reserves are "still ample," but recent funding market conditions suggest that the Federal Reserve may be nearing a critical point for ending balance sheet reduction
According to the Zhitong Finance APP, the reserves of the U.S. banking system have declined for eight consecutive weeks, falling below the $3 trillion mark for the first time, raising market concerns about whether the Federal Reserve will end its balance sheet reduction early. According to data released by the Federal Reserve on Thursday, for the week ending October 1, bank reserves decreased by $20.1 billion to $2.98 trillion, the lowest level since January of this year.
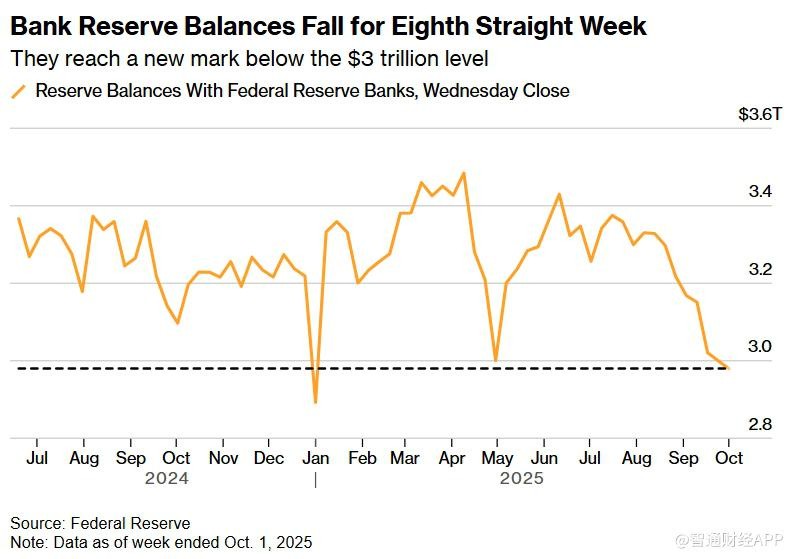
The decline in reserves is closely related to the U.S. Treasury's increased bond issuance. Since raising the debt ceiling in July, the Treasury has accelerated the issuance of government bonds to rebuild cash balances, absorbing market liquidity. This directly impacts the liability side of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet, including the overnight reverse repurchase (RRP) tool and commercial bank reserves. As RRP gradually depletes, commercial bank reserves held by the Federal Reserve have become the main "bleeding point," with foreign banks' cash assets declining faster than those of domestic U.S. banks.
This change comes as the Federal Reserve continues to implement quantitative tightening (QT). QT tightens liquidity in the financial system by reducing the holdings of government bonds and mortgage-backed securities (MBS). Earlier this year, the Federal Reserve slowed the pace of balance sheet reduction, decreasing the amount of maturing bonds each month to avoid triggering market turbulence.
Nevertheless, Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell stated last month that bank system reserves "remain ample" and that he expects the balance sheet reduction to end when reserves fall to "ample levels." However, recent signs in the funding market indicate that the Federal Reserve may be gradually approaching this critical point.
There is inconsistency within the Federal Reserve regarding the definition of "ample levels." Vice Chair Bowman reiterated last week that efforts should be made to shrink the balance sheet as much as possible, bringing reserves closer to "scarce" levels. Governor Waller estimated in July that the minimum reserve level is around $2.7 trillion

