
NVIDIA - The "Central Bank" of the AI Circle

NVIDIA shapes the AI ecosystem through massive cash flow, acting as a "last guarantor" when financing is difficult in data centers. This crazy investment stems from two major driving forces: huge cash reserves and a deep fear that technological breakthroughs may bypass its chips, attempting to deeply bind key participants
In the AI era, NVIDIA is no longer just a chip-selling company, but is transforming into a "central bank-like" entity that controls capital flows, influences technological directions, and stabilizes industrial ecosystems.
On September 27, the tech media The Information published an in-depth report analyzing the unique role of NVIDIA and its CEO Jensen Huang in the AI economy, revealing how NVIDIA has gradually become a "government-like" presence in the AI field through large-scale investments and strategic layouts.
The article showcases how this chip giant uses its massive cash flow to shape the entire AI ecosystem through in-depth research and interviews with several industry insiders, including NVIDIA executives and informed sources. The report points out that NVIDIA's investment strategy has surpassed traditional business cooperation and has begun to exhibit characteristics similar to government economic regulation.
The article argues that NVIDIA's scale and scope of investment have reached unprecedented levels. From data center construction to AI model development, from incubating startups to financing large projects, NVIDIA's reach extends to nearly every corner of the AI industry. This comprehensive participation has granted it a "central bank" status and influence in the AI economy.
The article particularly emphasizes the driving factors behind NVIDIA's frenzied investments—deep-seated fears that future technological breakthroughs may bypass its chips. This concern has prompted the company to adopt a more aggressive investment strategy, attempting to solidify its core position in the AI ecosystem through capital power.
The "Government" Role in the AI Economy
The article begins by mentioning Jensen Huang's dazzling investment moves, such as NVIDIA's commitment to invest up to $100 billion in OpenAI over the past few months, acquiring technologies and talents from several startups, and even extending an olive branch to competitor Intel. All these actions point to a core idea: NVIDIA is becoming the "de facto government" in the field of artificial intelligence.
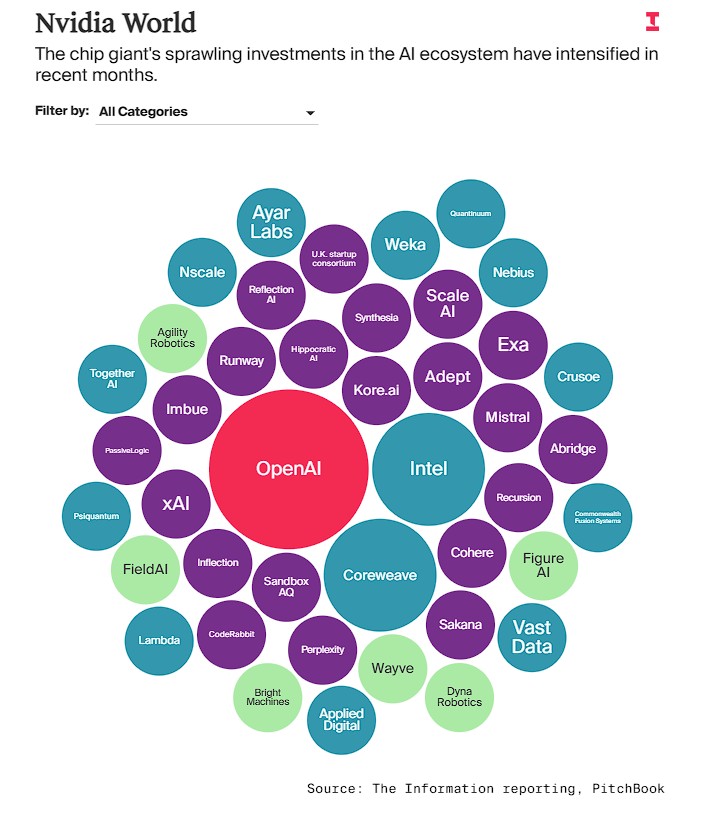
The article states that in September alone, NVIDIA completed several major investments: agreeing to acquire all unsold GPUs from cloud service provider CoreWeave over the next seven years, a deal that could cost around $6.3 billion.
In addition, NVIDIA invested $700 million in the UK data center startup Nscale, spent over $900 million to hire the CEO and engineers of network startup Enfabrica and obtain its technology licenses, and purchased a 4% stake in struggling chipmaker Intel, valued at $5 billion.
The most notable development this week is that NVIDIA expressed its intention to invest up to $100 billion in OpenAI over the next few years.
As part of the collaboration between the two companies, this AI startup will use the investment to build an AI data center that consumes at least 10 gigawatts of power, equivalent to 4 to 5 million NVIDIA GPUs—approximately the total number of GPUs NVIDIA plans to ship throughout 2025. As Jensen Huang stated this week on CNBC: "This is a huge project." "NVIDIA's investments have become so large and extensive, involving numerous companies across data centers, model creation, and other categories, that it is starting to resemble a 'government' in the field of artificial intelligence. This metaphor is not an exaggeration, but a true reflection of its influence in the AI ecosystem.
The amount of funding NVIDIA has injected into AI companies like OpenAI is approaching the level of government stimulus programs.
As the largest beneficiary, NVIDIA is reaping huge rewards from the booming AI economy, as its GPUs are at the core of training and running the most advanced large language models. The funding NVIDIA provides to AI startups helps them cover GPU costs, effectively bringing some cash back to the company in the form of chip sales.
Harvard Business School professor David Yoffie commented on this:
"They are working to stimulate demand for their products, which is a completely valid strategic direction. On the other hand, the scale of this investment and the fact that it is targeted at a single customer raises a question—are they stimulating artificial demand that cannot be sustained in the long term and may lead to serious negative returns in the future?"
Playing the Role of a "Central Bank" in the AI Field
Meanwhile, this investment behavior has also brought NVIDIA significant "soft power."
For example, Jensen Huang maintains good relationships with senior officials from multiple governments. When NVIDIA announced a series of investments in the UK, the British Prime Minister personally endorsed it, which undoubtedly helped ease the previously tense regulatory relationship due to the failed acquisition of Arm. This influence has transcended the commercial realm and begun to take on quasi-political characteristics.
Reports cite two informed sources revealing a behind-the-scenes story:
Recently, some large data center builders encountered difficulties in project financing, and traditional financial institutions began to become cautious. At this critical moment, NVIDIA stepped in.
The article directly quotes the source's viewpoint: "NVIDIA is willing to intervene and provide financing support to data center companies, which helps attract other project funders." In other words, NVIDIA's intervention is like a central bank injecting liquidity into the market, acting as a 'lender of last resort.'
Its credit endorsement and financial support greatly reduce the risks for other investors and invigorate the entire financing chain.
Although this behavior is aimed at ensuring the future sales of its GPUs, it objectively stabilizes market confidence and ensures that AI infrastructure construction does not stall. This is precisely the key role that central banks play in the financial system—preventing systemic risks from occurring.
Behind the Frenzied Spending: Fear and Huge Cash Reserves
What drives NVIDIA to invest so recklessly? The article suggests that there are two main driving forces behind it: enormous cash reserves and deep-seated survival fears.
First, NVIDIA is simply "too wealthy."
According to estimates from S&P Global Market Intelligence, NVIDIA's free cash flow is expected to reach $97 billion in fiscal year 2026 and $148 billion in fiscal year 2027. Just two years ago, in fiscal year 2024, NVIDIA's free cash flow was only $26.9 billion Due to regulatory constraints, it has become exceptionally difficult to spend this large sum of money through major mergers and acquisitions, making strategic investments the most logical expenditure choice for its massive cash reserves.
But a deeper reason is a fear that lingers among the company's executives.
The article cites the views of two NVIDIA executives, revealing an inescapable "terrifying scenario" within the company: "What if there is a significant breakthrough in the field of artificial intelligence that does not rely on NVIDIA chips?"
Some executives believe that would mark the beginning of the company's demise. They are particularly concerned that industry leaders like OpenAI might one day achieve the milestone of "de-NVIDIA-ization" first.
The article points out that this fear drives NVIDIA to bind key participants in the entire ecosystem to its chariot at all costs.
Artificially Created Prosperity?
At the same time, the article presents concerns and doubts about NVIDIA's strategy. Harvard Business School professor David Yoffie raises a pointed question:
Is NVIDIA's massive investment in a single customer (like OpenAI) stimulating real demand, or is it "stimulating artificial demand"?
He worries that this prosperity generated by suppliers may not be sustainable and could lead to severe negative returns in the future.
Yoffie further analyzes that NVIDIA's aggressive approach may force cloud computing giants like Amazon and Google to accelerate their own chip development efforts to reduce dependence on a single supplier.
"It's like an overly powerful ally that makes the king feel uneasy. Especially if OpenAI really uses this computing power to provide cloud services in the future, it will directly compete with Amazon and Google, making the relationship between NVIDIA and its major customers more delicate."
To support this point, Yoffie cites the historical lesson of Intel's decline. He mentions that when Apple began developing its own chips, few believed it would succeed, but it ultimately replaced Intel in Mac computers. This history is deeply etched in the memory of the tech industry.
He believes that Jensen Huang must subscribe to the famous saying of former Intel CEO Andy Grove— "Only the paranoid survive." This vigilance against potential disruptors is at the core of NVIDIA's strategy

